Vulnerability scanning is a key component of any effective cybersecurity strategy. It involves automated processes to detect software, systems, and network vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to patch security gaps before cybercriminals exploit them. As attacks grow more sophisticated, regularly scanning your environment is essential for protecting sensitive data, avoiding breaches, and meeting regulatory requirements.
What to Look For in a Vulnerability Scanner
When selecting a vulnerability scanner, an organization should look for seven key features in its chosen software solution. Let’s discuss them quickly.
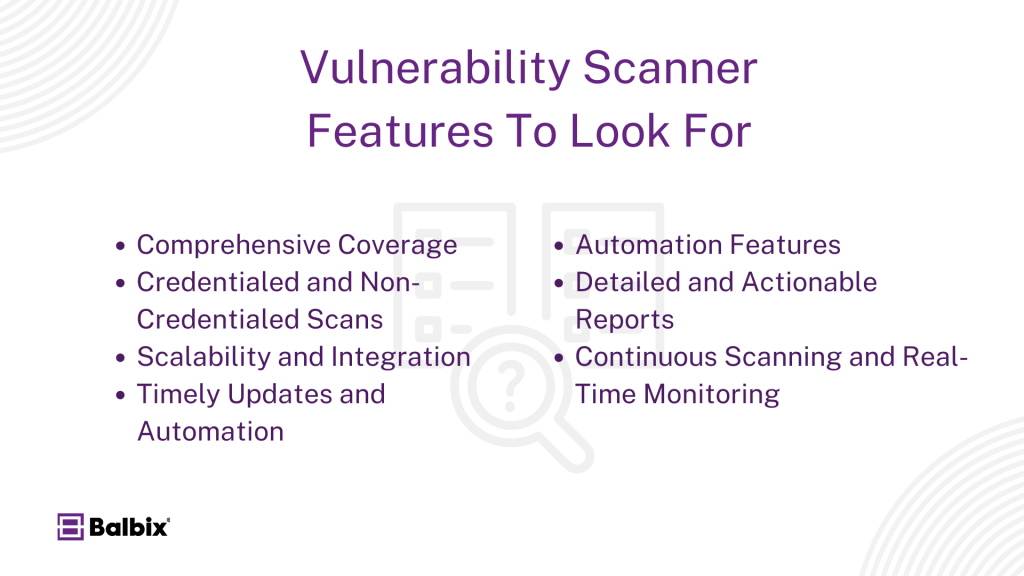
Comprehensive Coverage (Networks, Applications, Cloud): Organizations should prioritize tools that offer comprehensive coverage across their entire IT environment, including networks, applications, and cloud infrastructure.
Credentialed and Non-Credentialed Scans: The ability to perform credentialed and non-credentialed scans is essential for identifying a wide range of vulnerabilities, from system misconfigurations to deep-rooted application flaws.
Scalability and Integration: Scalability and ease of integration with existing security tools are also critical, ensuring the scanner can grow with the organization’s needs and seamlessly fit into its cybersecurity ecosystem.
Timely Updates and Automation: A reliable vulnerability scanner should also provide timely updates to stay ahead of emerging threats and offer detailed, actionable reports that help prioritize vulnerabilities based on severity and risk.
Automation Features: Automation is a key feature for vulnerability scanners. It lets them quickly detect and respond to vulnerabilities, helping organizations reduce manual intervention and remediate risks faster.
Detailed and Actionable Reports: Good vulnerability scanners find issues and provide detailed reports that help organizations prioritize fixes based on the severity of vulnerabilities, risk to business operations, and compliance requirements.
Continuous Scanning and Real-Time Monitoring: Some scanners offer continuous scanning capabilities, providing real-time monitoring to detect vulnerabilities as they appear, which is increasingly important in modern, dynamic environments.
10 Top Vulnerability Scanners
1. Nessus
Nessus, developed by Tenable, is one of the most trusted vulnerability scanners. Known for its versatility, Nessus excels at detecting vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance issues across a wide range of systems and applications. Its ability to perform credentialed and non-credentialed scans makes it a go-to solution for many organizations.
2. QualysGuard
QualysGuard is a cloud-based vulnerability scanner renowned for its scalability. It provides comprehensive scanning, reporting, and patch management, making it ideal for large enterprises. QualysGuard’s seamless integration with other security tools helps security teams efficiently identify and address vulnerabilities, ensuring they stay compliant with industry standards.
3. OpenVAS
OpenVAS, part of Greenbone Networks, is an open-source vulnerability scanner that offers a full-featured solution for organizations of all sizes. It regularly updates its detection capabilities to keep pace with new threats. It can also be used for intrusion detection, making it a flexible tool for cybersecurity professionals on a budget.
4. Rapid7 InsightVM
Formerly Nexpose, Rapid7 InsightVM delivers live monitoring and real-time insight into vulnerabilities. Its integration with the Rapid7 Insight platform enables detailed analytics and vulnerability management. The tool’s automation features and in-depth reporting help security teams prioritize critical risks and streamline remediation efforts.
5. Acunetix
Acunetix specializes in web application vulnerability scanning, making it ideal for organizations focused on web security. It detects common threats like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities while offering network scanning capabilities. Acunetix’s straightforward interface and automation features make it a popular choice for security testers and developers.
Stop Sabotaging Your Cybersecurity
Avoid the 11 common vulnerability management pitfalls

6. Nmap
Although widely recognized as a network discovery tool, Nmap also includes powerful vulnerability scanning features. Its scripting engine allows users to customize scans, making it an adaptable solution for identifying network, application, and service vulnerabilities.
7. ZAP (Zed Attack Proxy)
ZAP is an open-source tool developers favor for testing web applications during the development lifecycle. It helps identify security flaws early in the process, making it easier to fix issues before they reach production environments. ZAP’s broad community support and regular updates ensure it remains a reliable solution for vulnerability detection.
8. OpenSCAP
OpenSCAP is a free and open-source vulnerability and compliance scanner. It helps organizations ensure their systems align with security policies and standards by automating compliance checks. OpenSCAP is ideal for security teams who adhere strictly to regulatory frameworks like HIPAA and PCI-DSS.
9. BurpSuite
BurpSuite is a comprehensive platform to help security professionals, and developers test web applications for vulnerabilities. The platform includes various tools and features, such as an intercepting proxy, scanner, intruder, repeater, decoder, comparer, extender, and sequencer.
10. Core Impact
Core Impact is a comprehensive solution that combines vulnerability scanning with penetration testing. It allows organizations to simulate real-world attacks to validate vulnerabilities, giving security teams deeper insights into their potential impact and helping them strengthen their defenses.
Going Beyond Scanning with Balbix
While using multiple vulnerability scanners is essential in securing your systems, relying on periodic scans leaves gaps. Continuous, real-time monitoring of vulnerabilities is necessary to stay ahead of threats.
Balbix goes beyond traditional scanning tools by continuously identifying and inventorying all IT assets, including servers, desktops, IoT devices, and more. It analyzes vulnerabilities across your attack surface and prioritizes them based on five critical factors: severity, threats, asset exposure, business criticality, and security controls. Balbix’s automated processes ensure vulnerabilities are dispatched to risk owners for immediate or supervised mitigation.
Unlike scanners that offer a snapshot in time, Balbix provides ongoing analysis, enabling organizations to stay agile in responding to ever-changing threats. A more proactive approach can reduce cyber risk and improve security posture.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How do you choose a vulnerability scanner?
-
Choosing a vulnerability scanner involves assessing your security needs, considering the type of assets you need to scan (such as web applications, networks, or endpoints), evaluating the scanner’s compatibility with your systems, and considering factors like ease of use, support, and cost. Selecting a scanner that fits your budget, effectively identifies vulnerabilities, and helps in their remediation is critical.
- What are the three types of vulnerability scanners?
-
There are three primary types of vulnerability scanners: network-based scanners, which assess vulnerabilities in network devices and servers; web application scanners, focused on identifying security weaknesses in web applications; and host-based scanners, which evaluate the security of hosts or servers, checking for vulnerabilities in the operating system and installed software.
- What are the 4 main types of security vulnerability?
-
The four main types of security vulnerabilities are injection flaws, where malicious data is sent to an interpreter as part of a command or query; broken authentication, which allows attackers to use weak or stolen credentials; sensitive data exposure, involving inadequate protection of data in transit or at rest; and XML External Entities (XXE), where attackers can exploit vulnerable XML processors if security constraints are weak or misconfigured.