Vulnerability scanning is a crucial process within any comprehensive cybersecurity program. It involves the automated detection of security weaknesses in software, systems, and networks, allowing organizations to identify and address potential threats before attackers can exploit them. Vulnerability scanning is vital in managing cyber risks, helping businesses safeguard sensitive data and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Vulnerability scanning plays a pivotal role in a comprehensive vulnerability management program. It is a proactive mechanism for detecting and identifying weaknesses within an organization’s digital infrastructure. Modern cyberattacks are evolving at an unprecedented pace, making vulnerability scanning an essential tool for staying ahead of potential breaches.
How Vulnerability Scanning Works
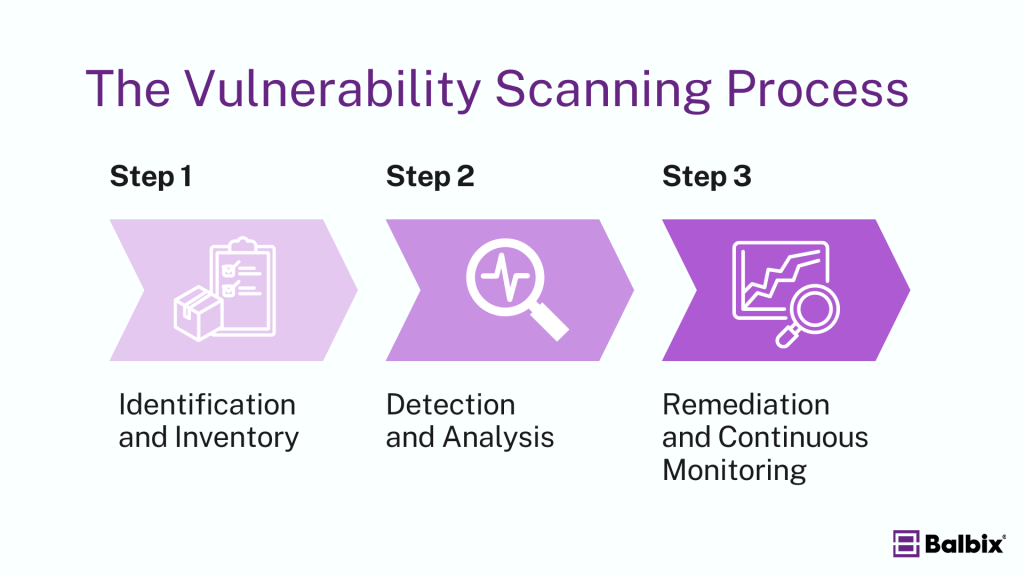
Vulnerability scanning follows a structured approach to identify and manage potential weaknesses in an organization’s IT infrastructure. Here’s how it works:
1. Identification and Inventory
The process begins with identifying and cataloging all systems, devices, and software within the organization. This comprehensive inventory helps create a detailed overview of the IT environment, serving as a critical foundation for the subsequent scanning and analysis.
2. Detection and Analysis
With the inventory in place, automated scanning tools detect vulnerabilities. These tools compare system configurations, software versions, and network settings against a database of known vulnerabilities. The detected vulnerabilities are then analyzed and categorized based on their severity, potential for exploitation, and impact on the business.
3. Remediation and Continuous Monitoring
Once vulnerabilities are identified, the next step is remediation, which involves applying fixes, updates, or changes to address the issues. After remediation, rescanning is performed to verify that the vulnerabilities have been effectively resolved. Continuous monitoring is then implemented to detect and address new vulnerabilities, ensuring ongoing protection.
What Vulnerability Scanning Reveals
Vulnerability scanning uncovers security gaps in an organization’s IT infrastructure, including:
- Weak points in systems that attackers could exploit.
- Outdated or unpatched software that creates vulnerabilities.
- Misconfigurations that may expose sensitive data or weaken defenses.
- Unnecessary open ports that can serve as entry points for attackers.
Why Vulnerability Scanning Matters
Vulnerability scanning is crucial because it helps organizations reduce cyber risk by identifying and fixing vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. It’s also essential for meeting industry regulations where regular scans are required to avoid fines and protect reputations. By addressing vulnerabilities early, companies can save money by preventing costly breaches and legal troubles.
Stop Sabotaging Your Cybersecurity
Avoid the 11 common vulnerability management pitfalls

Additionally, scanning clarifies an organization’s assets, helping them manage their IT environment more effectively. Ultimately, regular scanning strengthens overall security, reducing the chances of a successful attack.
How Vulnerability Scanning is Used
Vulnerability scanning can be applied across different areas, depending on the specific needs of the organization:
- Network Vulnerability Scanning identifies weaknesses in network infrastructure components such as firewalls, routers, and switches, which attackers could exploit to compromise the network.
- Web Application Vulnerability Scanning focuses on web applications. It detects flaws that could be targeted in attacks, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other common vulnerabilities in web-based applications.
- Database Vulnerability Scanning assesses the security of database management systems, highlighting vulnerabilities that could lead to unauthorized access or breaches of sensitive data.
- Host Vulnerability Scanning examines individual hosts, including servers and endpoints, for potential security gaps that attackers could exploit to gain unauthorized access or control.
Different Types of Vulnerability Scans
Active Scanning
Active scanning involves sending direct probes and requests to systems or devices to identify vulnerabilities. It provides detailed, in-depth information about exposed services, open ports, and potential misconfigurations. However, because it actively interacts with systems, it can consume bandwidth and might affect performance, making it best suited for periodic scans rather than continuous monitoring.
Passive Scanning
Passive scanning monitors network traffic without directly interacting with the systems. It identifies vulnerabilities based on observed data flows, detecting outdated software or insecure communication channels. Because passive scanning is non-intrusive, it can run continuously without impacting system performance. However, it offers a more limited scope, potentially missing internal misconfigurations or vulnerabilities not detectable through network traffic analysis.
Internal Scanning
Internal scans focus on systems within the organization’s network perimeter. They are vital for identifying vulnerabilities that internal threats, such as compromised insiders or malware, could exploit. Internal scanning identifies weaknesses external scans might overlook by examining devices, applications, and systems behind the firewall.
External Scanning
External scans assess internet-facing systems like web servers, cloud environments, and other public-facing assets. This scan type focuses on vulnerabilities external attackers could exploit, like open ports or insecure web applications. External scanning is critical for understanding an organization’s exposure to the wider internet and securing publicly accessible systems.
Authenticated Scanning
Authenticated scanning involves scanning systems with privileged access, such as using administrative credentials to log into the evaluated systems. This method allows the scanner to perform deeper analysis, revealing vulnerabilities in file systems, system configurations, and user privileges that may not be visible in unauthenticated scans. Authenticated scanning provides a comprehensive view of potential vulnerabilities, giving organizations more actionable insights for remediation.
Unauthenticated Scanning
Unauthenticated scanning operates without login credentials and assesses systems as an external attacker would—probing for vulnerabilities visible outside the system. This scan type identifies issues such as open ports, exposed services, and easily exploitable vulnerabilities but cannot detect deeper configuration problems or user-level weaknesses. While unauthenticated scans provide valuable insights into external risks, they are typically less thorough than authenticated scans.
Challenges of Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability scanning is an incredibly useful tool for identifying weaknesses in a system or network, but it comes with challenges. One of the main issues is the “snapshot effect,” where the scan only captures vulnerabilities that exist during the scan, potentially missing new issues that arise afterward.
Additionally, conducting comprehensive vulnerability scans often requires special access privileges, such as admin-level permissions, to examine all system parts thoroughly. Another limitation is that vulnerability scans typically focus on known issues, which may overlook new or unknown vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit, such as zero-day exploits.
Using Vulnerability Scanners
Vulnerability scanning is important for identifying and mitigating risks in today’s complex cybersecurity landscape. By taking a proactive approach to vulnerability management, organizations can improve their security posture, protect sensitive data, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Balbix simplifies this process with its advanced tools, providing proactive risk management and detailed insights to keep your systems secure and compliant.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Do you need a vulnerability scanner?
-
A vulnerability scanner is essential for identifying weaknesses in your systems, networks, or applications. It helps you proactively detect security flaws before attackers can exploit them, allowing your team to prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities, ultimately reducing your overall cyber risk.
- What is the difference between a vulnerability scanner and antivirus software?
-
A vulnerability scanner identifies security weaknesses in systems, networks, and applications, helping organizations patch vulnerabilities. Antivirus software, on the other hand, detects and removes malware from devices, focusing on known malicious threats. Vulnerability scanners prevent future attacks, while antivirus software addresses current threats.
- What is the most common type of vulnerability scan?
-
The most common type of vulnerability scan is a network-based scan, which assesses devices and systems on a network to identify security weaknesses. It helps detect vulnerabilities in open ports, misconfigurations, and outdated software, providing critical insights for prioritizing remediation efforts.