Security automation integrates various security tools, processes, and infrastructure to automate time-consuming and time-critical cybersecurity tasks. This approach reduces the reliance on manual intervention, allowing IT and security teams to scale their efforts efficiently. Security automation minimizes human error and enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks such as threat detection, incident response, and vulnerability management.
Security automation is transitioning from a luxury to a necessity. It empowers security teams to respond swiftly to emerging threats and streamline repetitive tasks so they can more easily focus on strategic, high-priority activities. Essentially, security automation optimizes security operations, helping organizations protect their assets and data more effectively.
How Does Security Automation Work?
Security automation replaces manual tasks with automated processes that detect, investigate, and respond to security incidents. Various tools, such as Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms, help automate workflows for activities like vulnerability management, threat intelligence, and incident response.
For example, in vulnerability management, security automation can automatically scan networks for vulnerabilities, prioritize them based on risk, and even apply patches or recommend remediation steps. This eliminates the need for constant manual monitoring and improves overall efficiency.
Benefits of Security Automation
Enhanced Efficiency
One of the standout benefits of security automation is its ability to boost efficiency significantly. By automating repetitive tasks—like data analysis and incident investigation—security teams can cut down on manual, time-consuming tasks and improve mean-time-to-patch (MTTP) and mean-time-to-respond (MTTR), alleviating security operations fatigue and enhancing overall productivity, agility, and operational efficiency.
Fast and More Accurate Threat Detection and Response
Manual processes are often fraught with the risk of human error, particularly when handling automation, which ensures that your defenses are always up-to-date and effective in a large amount of data. Security automation minimizes this risk by implementing consistent detection and quicker, more effective responses. Automation also shortens time-to-action for incident response and remediation, ensuring that threats are addressed swiftly and accurately halted, preventing further possible risks to business continuity.
Scalability
As organizations expand, so does their attack surface. Security automation equips teams to scale their defenses efficiently without the need for proportional increases in headcount. Whether managing thousands of endpoints or securing complex hybrid cloud environments, automation helps navigate and manage this complexity. It enhances operational speed across networks, storage, architecture, and security teams, enabling faster cycle times and more robust defenses.
Making GenAI Work for Cybersecurity
Join Nvidia and Balbix as they explore how to apply GenAI to cybersecurity, avoid common pitfalls, ensure data privacy, and uncover the true costs of building and maintaining a GenAI solution.



Cost-Effectiveness
Security automation delivers substantial cost savings by reducing the need for manual intervention. This reduction in operational costs allows resources to be redirected toward more strategic initiatives, such as improving overall security posture and planning. In essence, automation enhances efficiency and optimizes the cost-effectiveness of security operations.
Five Common Use Cases of Security Automation
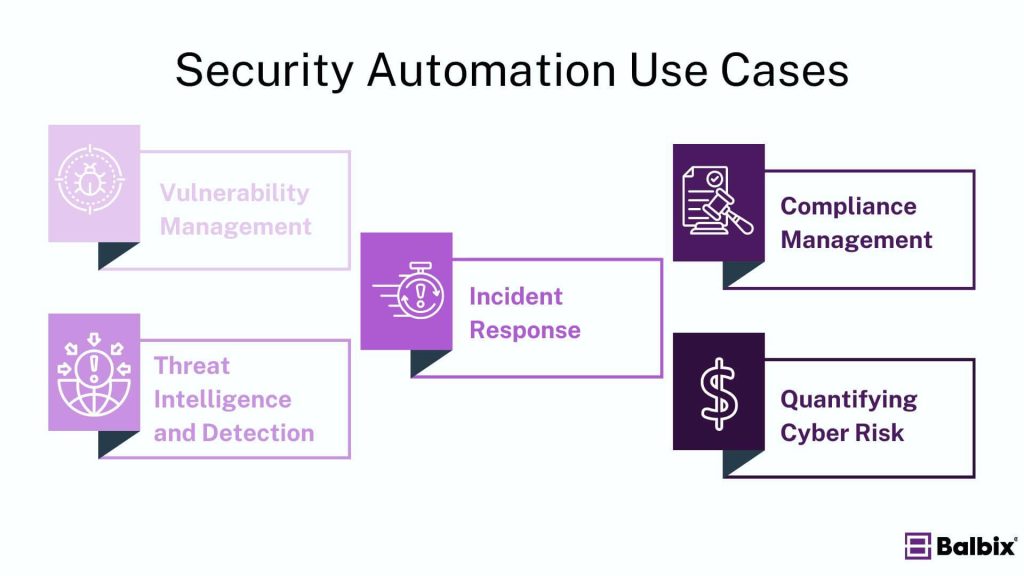
- Vulnerability Management: Automation ensures that your proactive defenses are always up-to-date and effective by continuously identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. This proactive approach minimizes potential security gaps and helps safeguard critical assets.
- Threat Intelligence and Detection: Security automation excels at real-time threat detection and actionable intelligence gathering. Automated systems tirelessly monitor your environment, delivering instant alerts for emerging risks and enhancing the fidelity rate of existing detection systems by feeding them with the latest threat intel.
- Incident Response: Automation transforms incident response by swiftly identifying, containing, and mitigating security threats in near real-time. This capability allows teams to react rapidly to attacks, limiting damage, minimizing disruption and improving the speed and effectiveness of incident management, resulting in a lower risk profile for the organization.
- Compliance Management: Maintaining compliance with industry regulations can take time and effort. Automated tools simplify this by providing continuous monitoring and reporting, ensuring that your organization adheres to necessary standards. This reduces the need for manual audits and helps avoid compliance-related pitfalls.
- Quantifying Cyber Risk: Security automation helps quantify cyber risk by providing a unified view of your asset inventory. This comprehensive perspective enables more accurate risk assessments and informed decision-making, helping you better understand and manage potential threats.
Security Automation Tools
A wide range of security automation tools is available to meet the diverse needs of organizations, regardless of size or industry. These tools fall into different categories based on their functions—some focus on managing and responding to attacks, while others aim to prevent breaches by automating various processes. Here are key examples of these tools:
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
XDR solutions combine data from various parts of the security environment—endpoints, networks, and cloud systems—to detect complex threats and attacks. These tools automate data collection and analysis, making it easier for analysts to investigate and respond to incidents. Critical features of XDR include:
- Centralized user interface (UI)
- Correlation of related alerts and data
- Continuous improvement
- Machine learning-based detection
- Automated response orchestration
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM systems gather and analyze security-relevant log data from an organization’s IT environment, such as system, application, firewall and database logs. They normalize this data into a standard format to allow the creation of detection content based on input from multiple disparate data sources, provide context for threat detection and hold historic data for retrospective threat hunting.
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR)
SOAR platforms automate the collection of alert-relevant threat data and incident response. They coordinate operations across multiple security tools, streamline automated workflows, and support policy execution and report automation. SOAR systems can also handle automated vulnerability management and remediation.
Unified Asset Inventory
Unified asset inventory tools continuously monitor and categorize assets across an organization—including devices, applications, and services—whether on-premises or in the cloud. These tools eliminate duplicate data, merge conflicting information, and enhance it with relevant business context, providing security teams with a comprehensive view of all their IT-related assets.
Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM)
RBVM tools automatically gather vulnerability data and add business context to prioritize risks effectively. They provide detailed remediation instructions, helping security teams respond more quickly, and reduce mean-time-to-patch (MTTP) and mean-time-to-respond (MTTR).
Challenges and Limitations of Security Automation
Despite its many benefits, security automation comes with challenges.
- Initial Setup and Continuous Management: Integrating and managing automation tools into existing infrastructure can be complex and time-consuming. Organizations must ensure the automation system meets the requirements for planned operational use, is compatible with their current setup, can support future technologies and is adaptable to changes in workflows.
- Over-Reliance on Automation: Human oversight is still critical, while automation can handle many tasks. Relying too heavily on automated processes can lead to missed nuances or threats that require human intuition.
Security Automation and AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming security automation by significantly enhancing its capabilities. AI-powered systems excel at analyzing vast amounts of data, learning from past incidents, and making informed real-time decisions. Machine learning algorithms improve detection capabilities, leading to faster and more accurate threat responses.
AI-powered security automation tools, like Balbix, provide sophisticated analytics and predictive insights, automating complex processes and enhancing the overall efficiency of security operations. This advanced approach ensures that your security infrastructure remains agile and effective in the face of evolving threats.
Best Practices for Implementing Security Automation
- Define Objectives and Scope: Start by pinpointing the processes that will gain the most from automation, such as routine tasks like patch management or log analysis. Conduct a thorough assessment to identify these high-impact areas. Carefully plan the automation rollout, considering the transition from manual to automated systems.
- Ensure Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure: Before deploying security automation tools, verify that they will integrate seamlessly with your existing infrastructure. Compatibility checks help prevent potential conflicts and ensure that the new tools enhance, rather than disrupt, your current security setup.
- Incorporate Training into the Rollout: Integrate training into your deployment plan for the teams managing the automation systems and those interacting with the output. Effective training ensures team members understand how to use the new tools and facilitates smooth interactions between automated systems and human operators.
- Monitor and Continuously Improve: Security automation should not be a “set it and forget it” approach. Regularly review and assess automated processes to ensure they meet objectives and function as intended. Monitor, test, and refine systems to adapt to new threats and optimize performance.
The Future of Security Automation
The future of security automation is closely tied to the growth of AI and machine learning. As these technologies evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated automated security systems capable of predicting and preventing threats with minimal human intervention. In a world where the cyber threat landscape is constantly shifting, security automation will remain a critical asset for organizations of all sizes.
Explore how Balbix’s exposure management platform can help you integrate security automation into your cybersecurity strategy, ensuring a proactive and resilient defense against cyberattacks.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How does security automation benefit organizations?
-
Security automation helps organizations improve efficiency, reduce response times, and minimize human errors in threat detection and response.
- What tasks can be automated in cybersecurity?
-
Typical tasks include threat detection, vulnerability, incident response, and patch management.
- Is security automation suitable for small businesses?
-
Security automation can help small businesses streamline security processes, improve threat detection, and reduce resource strain.
- How does security automation integrate with existing security tools?
-
Security automation platforms integrate with existing tools, such as firewalls, SIEM systems, and EDR Systems, to automate tasks and improve coordination.