Security analytics analyzes security data using advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect patterns and anomalies indicative of cyber threats. This approach empowers organizations to proactively identify and mitigate potential risks by transforming vast raw security data into actionable insights.
Security analytics solutions collect and aggregate data from various sources, including system and application logs, network traffic, threat intelligence feeds, and endpoint data. Advanced analysis techniques, such as statistical analysis and machine learning algorithms, are applied to this data to identify correlations and anomalies indicating malicious activity and anomalies worth investigating further.
Security analytics solutions focus on preventing the next attack, addressing hidden vulnerabilities, and closing identified security gaps, ensuring organizations stay one step ahead of cybercriminals.
How do Security Analytics work?
Security analytics solutions empower organizations to gain in-depth insights into their security posture and potential risks.
For real-time incident detection and response, security analytics solutions continuously ingest data captured from events and alerts throughout the network (e.g., endpoint and user behavior data, applications, operating system event logs, firewalls, routers, network traffic analyzers, virus scanners, threat intelligence feeds, and contextual data).
This information is analyzed to proactively detect intrusions by hunting for anomalies such as malware, ransomware, suspicious traffic, or unusual application usage if configured correctly, and this can lower the false positive rate than if you rely on isolated events from a single security control.
Security analytics solutions quantify organizational risk and prioritize risk mitigation activities for accurate security posture management. They ingest and analyze data from asset inventories, software bill of materials (SBOM), configuration management databases (CMDBs), cloud environments, vulnerability scans, and other relevant IT and security tools.
Using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Security Analytics
So, why use AI and ML for continuous analysis?
The sheer volume of data that any given environment produces might contain suspicious event information that security teams should investigate but is hard to find manually. Having secOpsdo do repetitive work 24/7 becomes counterproductive, and it is impossible to guarantee consistency and continuity.
The burden on teams to do the same thing repeatedly can be best eliminated by applying AI and ML. It decreases the fatigue and burnout rate of security teams, allows for better consistency around the clock and frees up time to focus on progressing an organization’s security stance.
For example, they can allow security teams to detect a cyber attack early at a much lower False Positive rate and gain actionable insights for stopping future threats. Similarly, advanced AI and ML algorithms can help organizations build unified risk models that analyze their cyber risk, predict likely breach scenarios, calculate breach impact in dollars, and develop action plans to improve their security posture and prevent the success of cyber attacks.
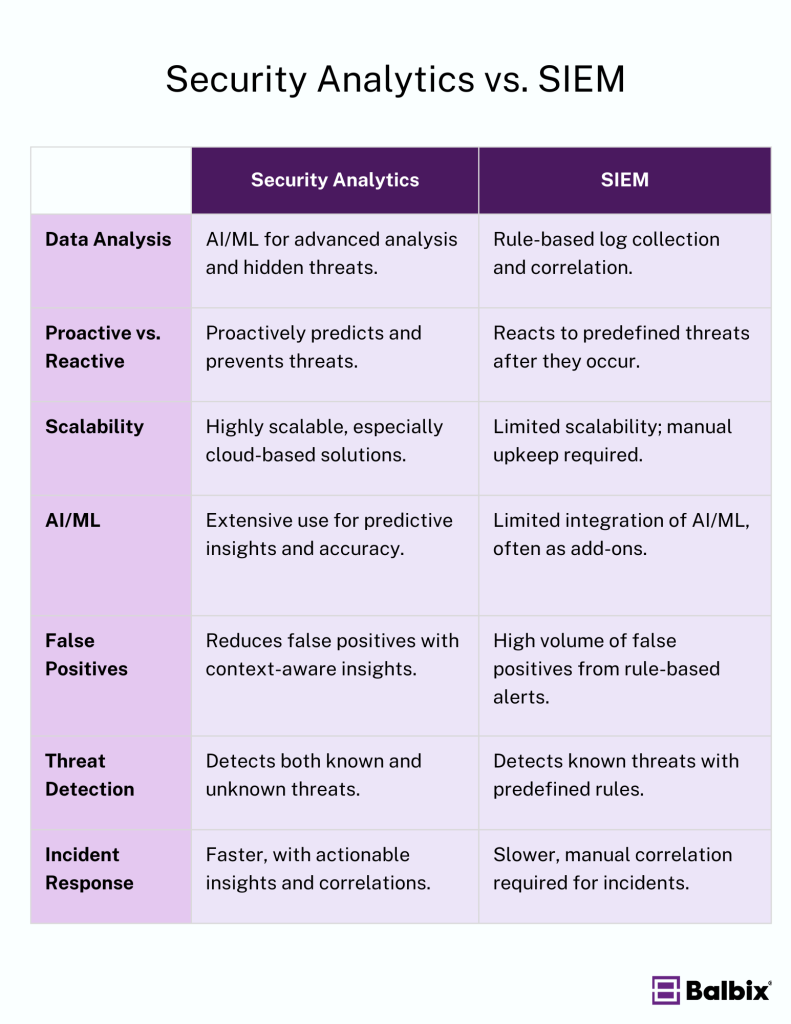
Security Analytics vs. SIEM: Understanding the Differences
While Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems have been a cornerstone in cybersecurity for aggregating log data and detecting threats, security analytics provides advanced analysis and actionable insights.
SIEM Solutions
- Real-time Monitoring and Logging: SIEM systems are designed to deliver real-time security monitoring, cyber threat detection, and incident response orchestration capabilities. They collect and store security-related log data from various sources, including network devices, cloud-based applications, and security tools.
- Compliance and Auditing: SIEM tools help aggregate data for compliance and auditing purposes, providing a unified view of events and information. This aids in tracking and responding to threats and demonstrating security due diligence.
- Alert Fatigue: Traditional SIEM tools often generate a high volume of alerts, which can lead to alert fatigue. This is because correlation rules can result in many false positives.
Making GenAI Work for Cybersecurity
Join Nvidia and Balbix as they explore how to apply GenAI to cybersecurity, avoid common pitfalls, ensure data privacy, and uncover the true costs of building and maintaining a GenAI solution.


Security Analytics
- Advanced AI and Machine Learning: Security analytics utilizes advanced AI and machine learning to analyze large datasets. This approach helps identify patterns and threats without prior definitions or attack signatures, enhancing detection accuracy.
- Context-Aware Insights: Security analytics provides context-aware insights, reducing the number of false positives. Security analytics can offer more precise threat detection by analyzing user behavior, network traffic, and other data points.
- Predictive Analytics: Security analytics enables predictive analytics to identify potential threats before they materialize. This proactive approach allows organizations to take preventive measures, enhancing their overall cybersecurity posture.
- Visibility and Coverage: Security analytics provides a holistic view of IT environments, including application programming interfaces and legacy solutions, not confined to narrow bands of visibility tied to specific attack signatures. This enhances the visibility and coverage of security measures.
- Handling Modern Threats: Security analytics is better suited to handle modern threats, including zero-day attacks and lateral movement within networks. It uses advanced analytics to detect and respond to these threats more effectively.
Key Differences
Data Analysis
Security analytics focuses on deep data analysis, using AI and machine learning to uncover hidden relationships, anomalies, and trends in large datasets. This enables more advanced threat detection than traditional methods.
While SIEM systems were initially built for log collection and correlation, next-generation SIEMs increasingly integrate AI and ML to move beyond basic correlation rules and improve detection capabilities.
Proactive vs. Reactive
Security analytics leans more towards a proactive approach, using historical and real-time data to predict potential threats and enable early detection. This approach allows organizations to take preventive action before incidents occur or minimize any damage inflicted by a successful breach that can result in financial loss.
In contrast, traditional SIEM tools have a more reactive approach with pre-built correlations that restrict themselves to the known knowns. Security teams are alerted after an event that has been expected and preconfigured to alert beforehand. Focusing on known threats based on predefined rules or signatures with an SIEM system helps teams have a single pane of glass. However, due to budget constraints, not all data will be stored in the SIEM for correlation.
This eventually results in the inability to eliminate manual correlation efforts, dashboard pivoting, and missed security events.
This is why SIEMs increasingly rely on Extended Detection & Response (XDR) type features and adopt AI-driven features.
Scalability
Security analytics solutions, especially cloud-based ones, are designed to handle vast amounts of data from today’s complex networks. They offer nearly unlimited scalability and storage, making them well-suited for modern enterprises.
Cloud-based security analytics tools mostly leverage an API to interconnect existing toolsets with valuable data to be analyzed in near real-time. Compared to a SIEM, this results in much quicker deployment and time-to-value. Modern SIEM solutions offer cloud-based options that improve scalability, reduce deployment times and eliminate uptime issues. But even after that, there is still much manual work to keep it operational, consistent, and reliable.
Benefits of Security Analytics
Security analytics relies on machine power to analyze diverse data sources, correlating incidents and events to detect real-time threats. This enables organizations to identify insider threats through user behavior analytics and recognize suspicious activities, compromised credentials, lateral movement, and data exfiltration early in the attack chain, allowing teams to respond more swiftly and investigate more effectively.
It provides a unified view of the security landscape by integrating all comprehensive data sources within an environment and swiftly applying multiple complex purpose-built AI models. It allows for including all data from critical data sources while maintaining scalability. AI and machine learning are crucial in maintaining operational consistency in this process.
Security Analytics Use Cases
Threat Detection and Response
Security analytics allow for more accurate alerting by proactive analysis of relevant security data generated by existing tools to pinpoint suspicious activity, identify improper account usage or compromise, detect data exfiltration by attackers, and immediately create security alerts to ensure a rapid response to cyber attacks.
Additionally, security analytics can detect insider attacks by monitoring users’ activities and identifying abnormal behaviors, such as unusual login times, unauthorized database requests, abnormal email usage, and unauthorized downloads or copying of sensitive data. In addition, security analytics assists organizations with adhering to government guidelines and regulations related to data storage and protection.
Assessing Risk and Improving Risk Posture
Aside from threat detection and response, security analytics assess an organization’s risk posture and improve its readiness to react to and recover from security events. With security analytics, organizations can accurately discover and inventory all IT assets, identify and prioritize risks through continuous vulnerability assessment and quantify cyber risk in dollars.
In addition, security analytics analyze different remediation scenarios to identify and prioritize strategies that efficiently address an organization’s most critical security issues to burndown cyber risks effectively
What to Look for in a Security Analytics Tool
To detect and respond to threats, organizations can use the following security analytics tools:
- Behavioral analytics tools gather data from many sources and identify user, application, and device behavior patterns that indicate a security threat due to anomalous activity.
- Forensic security analytics tools investigate past or ongoing attacks, identify the cause of compromises, and help remediate vulnerabilities.
- Network analysis and visibility (NAV) applications or devices analyze network traffic from end-users and applications. This includes network discovery, flow data analysis, metadata analysis, packet capture and analysis, and network forensics.
- Compatibility with your existing and possible planned expansion of toolsets in the upcoming years.
To assess risk and improve security posture in conjunction with security analytics, organizations can use the following cyber risk management tools:
- Cyber asset attack surface management (CAASM) tools continuously ingest data from IT and security tools to create a unified view of all assets within an organization. Asset criticality is incorporated into the data sets to help analyze cyber risk.
- Vulnerability assessment tools are designed to continuously scan systems to identify and prioritize vulnerabilities by leveraging CVSS scores.
- Cyber risk quantification tools unify cybersecurity data into a model that calculates cyber risk in dollars, helping organizations allocate resources and prioritize mitigation actions.
Security analytics solutions such as Balbix can calculate each point of this attack surface and produce relevant insights about your cyber risk.
Additionally, Balbix allows the creation of dashboards for each stakeholder, enhancing visibility and enabling actionable insights for improved threat detection and response. These dashboards focus on three main areas: asset inventory, risk-based vulnerability management, and cyber risk quantification.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why is security analytics important?
-
Security analytics is the next step for organizations to protect critical information by analyzing real-time threats, risks, and security levels. It’s essential for spotting potential threats and evaluating an organization’s readiness to prevent cyber attacks. By offering a comprehensive view of the organization’s vulnerabilities and the likelihood of a breach, security analytics give security teams the necessary insights and data for making informed decisions.
- Does your company need security analytics?
-
All organizations need security analytics due to growing cyber threats, increased complexity and the rise of adversarial AI. This helps identify threats, protect sensitive data, and improve overall security, which allows an organization to adapt quickly and reduce the likelihood of a breach. It’s becoming increasingly crucial to detect sophisticated attacks and leverage AI and ML to prevent future cyber attacks.


