Penetration testing, often called “pen testing,” is a proactive security measure that involves simulating cyberattacks on a system, network, or application to uncover vulnerabilities before malicious actors exploit them. These tests help organizations identify weaknesses in their cybersecurity defenses, allowing them to address and mitigate risks before they become threats.
By testing the resilience of your systems, pen testing provides valuable insights into how adequate your existing security controls are and what steps need to be taken to improve them.
Why is Penetration Testing Important?
Penetration testing is critical for organizations of all sizes because it offers a real-world evaluation of cybersecurity defenses. Rather than relying on theoretical assessments, pen testing shows how attackers could exploit vulnerabilities in your network, systems, or applications. This practical approach enhances an organization’s ability to anticipate and mitigate potential breaches.
Here’s why penetration testing is important:
- Identifies vulnerabilities: Pen testing uncovers hidden flaws and weaknesses in systems, applications, or networks that automated scans might miss.
- Mitigates risks: By discovering vulnerabilities, organizations can address them before attackers exploit them, reducing overall risk.
- Enhances security posture: Regular pen testing keeps systems up-to-date with the latest threats and exploits, improving overall security resilience.
- Compliance and regulation adherence: Many industries require regular pen testing to meet regulatory requirements, safeguard sensitive data and maintain trust.
Pen Testing and Compliance
For many organizations, penetration testing isn’t just a good security practice—it’s a requirement. Various regulations mandate regular pen testing to ensure that sensitive data remains secure. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. Therefore, penetration testing is vital in meeting compliance standards and demonstrating due diligence in safeguarding critical assets.
Who Performs Pen Tests?
Cybersecurity professionals with specialized knowledge and tools typically carry out penetration tests. These professionals, often known as ethical or white-hat hackers, use the same techniques and strategies as malicious hackers but with permission and a clear goal: to identify and fix security weaknesses.
Some organizations may have internal security teams trained to conduct pen tests, while others outsource this task to third-party cybersecurity firms. Third-party testers benefit from providing an unbiased assessment, as they aren’t familiar with the system’s inner workings.
What Are the Types of Pen Tests?
Penetration testing comes in various forms, each designed to address specific security needs. The types of pen tests include:
Open-Box Pen Test
In an open-box pen test, the tester is provided with complete information about the target system, including architecture details, source code, and network diagrams. This type of test mimics the insider threat scenario, where attackers have insider knowledge of the system.
Closed-Box Pen Test (Blind Test)
A closed-box, or blind test, involves minimal information provided to the tester. The ethical hacker knows little to nothing about the target system, similar to an external attacker without insider knowledge. This test simulates how a hacker might gather information from the outside and identify weaknesses.
Covert Pen Test (Double-Blind Test)
In a covert or double-blind pen test, neither the security team nor the ethical hacker is aware of the specific time or scope of the test. This test evaluates an organization’s security team’s detection and response capabilities, simulating a real-world attack scenario.
External Pen Test
An external pen test focuses on the vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit outside the organization. It targets public-facing systems such as websites, email servers, and firewalls to identify potential entry points.
Internal Pen Test
Internal pen testing evaluates what an attacker could do with access to an organization’s internal network. This could simulate the actions of a rogue employee or someone who has breached external defenses and gained insider access.
What Are the Stages of Pen Testing?
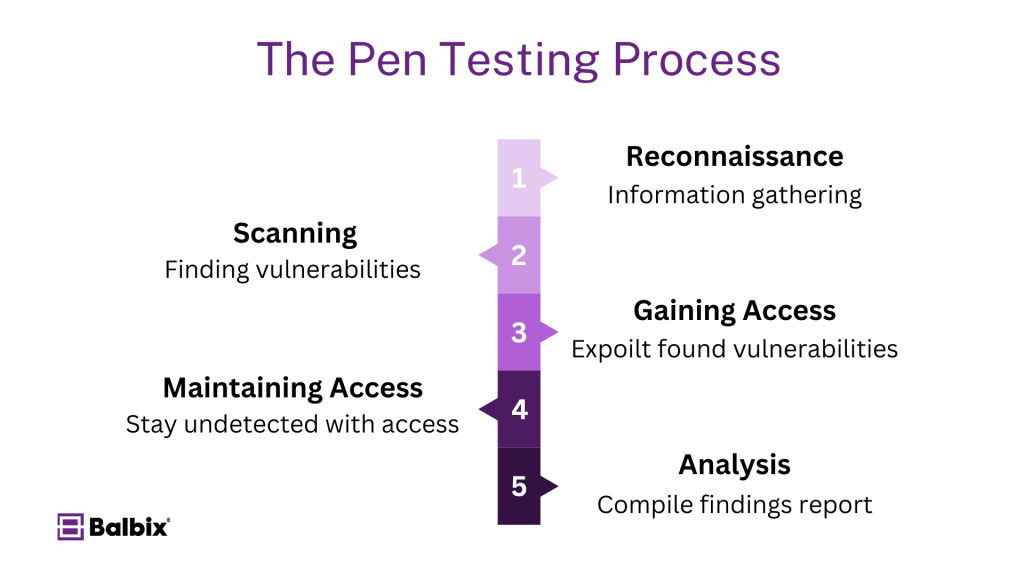
Penetration testing follows a systematic approach to uncover vulnerabilities, typically progressing through the following stages:
1. Reconnaissance
During reconnaissance, the tester gathers information about the target system or network. This may include domain names, IP addresses, open ports, and system architecture. The goal is to gather as much data as possible to understand the attack surface.
2. Scanning
In the scanning phase, the ethical hacker uses tools to analyze the target for vulnerabilities. This could involve network, port, and vulnerability scanning to identify weak points that could be exploited.
3. Gaining Access
Once vulnerabilities are identified, the tester attempts to exploit them to gain unauthorized access to the system. This stage involves using various methods, such as SQL injection, password cracking, or buffer overflow attacks, to penetrate the system.
4. Maintaining Access
After gaining access, the ethical hacker tries to maintain access to the compromised system without detection. This simulates how real attackers operate to carry out extended attacks, steal sensitive data, or compromise additional resources.
5. Analysis
In the final stage, the ethical hacker compiles all findings into a detailed report. This report includes the vulnerabilities discovered, the methods used to exploit them, and recommendations for remediation. The organization can then fix the vulnerabilities and enhance its security posture.
Making GenAI Work for Cybersecurity
Join Nvidia and Balbix as they explore how to apply GenAI to cybersecurity, avoid common pitfalls, ensure data privacy, and uncover the true costs of building and maintaining a GenAI solution.


What Are the Pros and Cons of Pen Testing?
Penetration testing provides numerous benefits, but it also has some limitations. Below are the pros and cons of pen testing:
Pros:
- Real-world risk identification: Pen tests simulate real-world attacks, providing actionable insights into how systems can be breached.
- Improved security posture: Pen testing helps organizations fix vulnerabilities and improve their defenses.
- Regulatory compliance: Regular pen testing ensures compliance with industry standards and legal regulations.
- Proactive defense: By identifying weaknesses before attackers can exploit them, pen testing provides a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
Cons:
- Cost: Penetration testing can be expensive, mainly by third-party professionals or on a large-scale system.
- Limited scope: A pen test typically focuses on specific areas and may not cover the entire system, leaving potential vulnerabilities unchecked.
- Time-consuming: Conducting thorough pen tests, particularly covert or double-blind tests, can take significant time and resources.
In summary, penetration testing is vital to a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. It helps organizations uncover weaknesses, comply with regulations, and bolster their defenses. Although it has some challenges, proactive vulnerability identification and mitigation benefits outweigh the costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the 5 stages of penetration testing?
-
The five stages of penetration testing are:
- Reconnaissance – Gathering information about the target.
- Scanning – Identifying potential entry points.
- Exploitation – Attempting to breach the system.
- Reporting – Documenting findings and vulnerabilities.
- Remediation – Offering solutions to fix identified vulnerabilities.
- What is a penetration test example?
-
A common example is a network penetration test, where a tester attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in an organization’s network infrastructure, such as open ports or weak passwords, to assess security and recommend necessary defenses.
- What is the role of a penetration tester?
-
A penetration tester simulates cyberattacks to identify and exploit system, network, or application vulnerabilities. Their role is to assess the effectiveness of security measures, report findings, and provide recommendations to strengthen defenses.
- Who needs penetration testing?
-
Organizations handling sensitive data, such as financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies, need penetration testing. Any business with valuable digital assets or compliance requirements can benefit from regular security assessments to ensure resilience against attacks.
- Who uses penetration testing?
-
Cybersecurity professionals, IT teams, and security consultants use penetration testing to evaluate the security of systems and applications. Industries like finance, healthcare, retail, and government agencies commonly employ penetration testing to safeguard sensitive data and comply with regulations.