Developed by the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST), the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS) is an advanced methodology used to predict the likelihood of exploiting a vulnerability. Using real-time data and machine learning, EPSS assigns a probability score to vulnerabilities so that organizations can prioritize the most imminent threats.
Unlike other scoring systems that assess the severity of a vulnerability, EPSS is all about the probability of actual exploitation; it’s a practical approach to vulnerability management.
History of the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS)
EPSS was introduced in 2019 as a response to the skyrocketing number of vulnerabilities. While thousands of new vulnerabilities are discovered yearly, only a small fraction of them are actually exploited in the wild — meaning that the exploit could pop up at any time.
While traditional vulnerability scoring systems, such as the CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System), can assess a vulnerability’s potential impact, they cannot predict its likelihood of exploitation.
Making GenAI Work for Cybersecurity
Join Nvidia and Balbix as they explore how to apply GenAI to cybersecurity, avoid common pitfalls, ensure data privacy, and uncover the true costs of building and maintaining a GenAI solution.


EPSS was designed to fill this gap, using real-time data and statistical modeling to predict which vulnerabilities will likely be attack targets.
How EPSS Works
Three key things to know about how EPSS works are where data comes from, how vulnerabilities are scored, and the positives/negatives.
Data collection and analysis
EPSS gets its information from multiple data sources, including threat intelligence feeds, public exploit databases, and malware repositories. EPSS models continuously update these datasets and can adjust vulnerability scores when new threats are discovered. Its dynamic and adaptive approach allows for more accurate predictions based on real-time events.
Scoring methodology
The EPSS model assigns a score between 0 and 1, corresponding to the likelihood that a vulnerability will be exploited within 30 days. Scores closer to 1 indicate a higher probability of exploitation.
The scoring algorithm considers various factors, including the existence of a public exploit, the type of vulnerability, and the target environment.
True positives, false positives, and false negatives
Accuracy for EPSS is all about separating the positives and negatives.
True positives occur when EPSS correctly predicts that a vulnerability will be exploited, while false positives mean that a vulnerability is expected to be exploited but is not. False negatives represent vulnerabilities not flagged as high risk but later exploited.
EPSS vs. CVSS
While EPSS and CVSS serve different purposes in vulnerability management, they are often (and should be) used together.
EPSS provides a predictive probability score that predicts the likelihood of a vulnerability being exploited in the near future. As noted above, it is dynamic and continually updated based on new threat intelligence and real-world events.
CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System), on the other hand, assesses the severity of a vulnerability and provides a static score that indicates how much damage a vulnerability could potentially cause. CVSS takes into account factors like attack vectors and complexity. It gives a score from 0 to 10 based on several metrics, including the complexity of the attack, the privileges required, and the potential impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Here’s an analogy. If EPSS and CVSS were on Star Trek’s Enterprise, CVSS would be like the ship’s threat assessment scanner, while EPSS would be like the ship’s behavioral analysis system. CVSS tells the crew how dangerous an alien ship could be (it’s a Borg cube!), while EPSS tells them how likely it is to attack (but it’s dormant, and there have been no reports of Borg activity in this sector).
Combining both systems can provide a more holistic approach to vulnerability management. It allows organizations to prioritize vulnerabilities based on their likelihood of exploitation and potential damage.
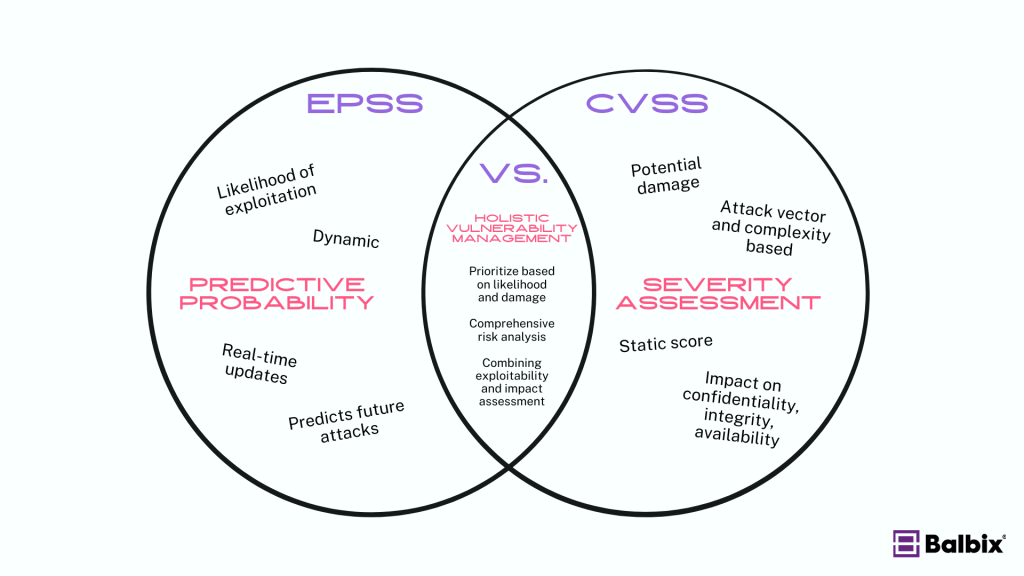
Is Combining EPSS with CVSS comprehensive enough?
While EPSS and CVSS can complement each other, using them together doesn’t guarantee complete protection. When combined, organizations gain a clearer picture of both impact and risk. However, neither system accounts for specific organizational contexts, such as a system’s unique configuration or the value of assets at risk.
For a comprehensive approach, security teams should also consider other factors, such as asset criticality, network segmentation, and mitigating controls.
The Challenges of EPSS
While EPSS offers significant benefits by predicting the likelihood of exploitation, several challenges remain.
Data limitations
EPSS relies heavily on publicly available data sources, such as threat intelligence feeds, exploit databases, and malware samples. However, if certain vulnerabilities have not been widely publicized or their exploit data is incomplete, the EPSS score may not accurately reflect the real-world risk.
For example, zero-day vulnerabilities that have not yet been disclosed will not have enough data to generate an EPSS score, potentially leaving organizations vulnerable to hidden threats. Plus, regional or sector-specific threats may not be fully captured in the global datasets that EPSS relies on.
Dynamic scoring
EPSS scores are constantly updated based on new data and real-time threat intelligence. While this makes the system highly adaptive, it also introduces complexity in decision-making. For example, a vulnerability that scored low in the morning might become a high-risk issue by the afternoon due to the emergence of a new exploit. For security teams already overwhelmed by a flood of alerts and information, tracking these fluctuations and responding in real-time can be challenging.
Margin of error
Like any predictive model, EPSS is not perfect. As mentioned above, false positives (vulnerabilities predicted to be exploited but aren’t) and false negatives (vulnerabilities not flagged but eventually exploited) are inherent risks to be aware of. These errors can confuse security teams, causing unnecessary remediation efforts or missed opportunities to patch vulnerabilities before exploitation. Teams must supplement EPSS with human expertise and additional context to minimize these risks.
Integration with existing processes
Many organizations have mature vulnerability management processes built around CVSS or other scoring systems. Integrating EPSS into these workflows can be difficult, as teams must determine how to prioritize vulnerabilities using EPSS and CVSS. Because not all vulnerability management tools support EPSS natively, they may require additional customization or tools to take full advantage of its capabilities.
Focus on exploitation and not impact.
While EPSS provides valuable insights into the likelihood of exploitation, it doesn’t assess the potential impact of a vulnerability on an organization. For example, a low-scoring vulnerability in EPSS could still have severe consequences if exploited in a critical system or environment.
How Balbix can help organizations using EPSS
Using EPSS should be part of a broader strategy for managing cybersecurity risk. Balbix helps organizations enhance vulnerability management by combining predictive analytics like EPSS with a comprehensive understanding of asset value, exposure, and impact.
With Balbix, organizations can:
- Automatically correlate EPSS scores with asset criticality and business impact.
- Leverage real-time data to stay ahead of emerging threats and make informed decisions about patching and remediation.
- Integrate EPSS and CVSS into a unified risk management platform that includes security controls when calculating risk.
- Continuously monitor the environment for new risks and adjust defenses on the go.
Using Balbix’s advanced AI-powered exposure management platform, security teams can bridge the gap between likelihood and impact and ensure their vulnerability management efforts are efficient, effective and accurate.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can you use EPSS and CVSS together?
-
Yes, you can use EPSS and CVSS together. EPSS predicts exploit likelihood, while CVSS assesses severity. Together, they provide a mostly comprehensive risk perspective.
- Which is better: EPSS or CVSS?
-
EPSS predicts the likelihood of a vulnerability being exploited, while CVSS scores the severity of vulnerabilities. Your choice depends on what you prioritize: likelihood or impact.
- What is the scoring range of EPSS in cybersecurity?
-
EPSS assigns CVEs a score between 0 and 1, and scores closer to 1 indicate a higher probability of exploitation within the next 30 days.