Security posture refers to an organization’s overall cybersecurity readiness, reflecting how well it can identify, protect, detect, respond to, and recover from security threats. This encompasses your systems, networks, policies, and controls, offering a holistic view of your cybersecurity readiness. A strong security posture provides the foundation for safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining cyber resilience.
Why is a Strong Security Posture Important?
A strong security posture has become more critical than ever for several key reasons:
- Protection Against Cyber Attacks: A strong security posture helps defend against various threats, including ransomware, phishing attacks, and data breaches. Without effective protection, sensitive information can be compromised, leading to severe financial and reputational damage.
- Adaptability to Future Attacks: Cybercriminals continually develop new tactics. An organization’s ability to adapt security measures ensures resilience against future threats. Maintaining a strong security posture enables businesses to evolve with these threats, preventing system weaknesses from exploitation.
- Effective Incident Response and Recovery: Organizations with strong security postures can detect breaches faster and respond more effectively, reducing the damage caused by cyber incidents. A well-prepared incident response plan enables rapid recovery of normal operations after an attack.
- Cost Savings in a Data Breach: A cyberattack has a significant financial impact. However, businesses with strong security measures can often mitigate the costs associated with breaches, including data loss, operational downtime, and regulatory penalties.
The Key Components of a Security Posture
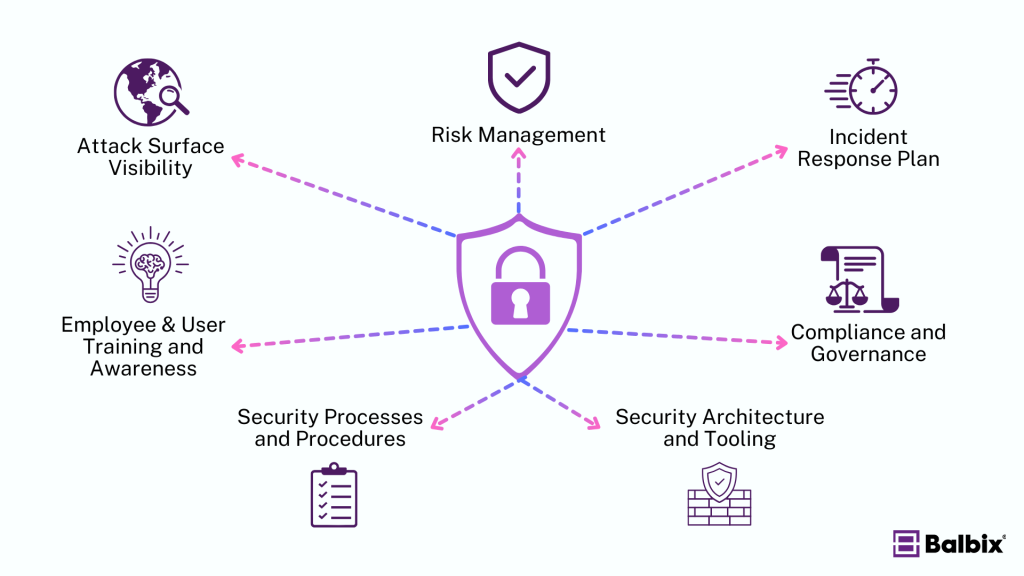
It’s important to break down the core elements of a security posture, which, when combined, provide a comprehensive view of how prepared you are to face cybersecurity challenges:
Attack Surface Visibility
The attack surface refers to all points where an attacker could exploit vulnerabilities. Effective visibility of your attack surface ensures that you understand the scope of potential risks across networks, devices, users, and applications.
Making GenAI Work for Cybersecurity
Join Nvidia and Balbix as they explore how to apply GenAI to cybersecurity, avoid common pitfalls, ensure data privacy, and uncover the true costs of building and maintaining a GenAI solution.


Risk Management
This involves identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks based on their potential impact. Risk management ensures your organization understands which vulnerabilities pose the most significant threat and which mitigation efforts should take precedence.
Incident Response Plan
A comprehensive incident response plan allows your organization to react promptly to security incidents, limiting damage and ensuring swift recovery. Effective incident response is vital for minimizing the fallout from a cyber event.
Compliance and Governance
Many industries must comply with specific cybersecurity regulations and frameworks. Ensuring governance and compliance within your security strategy helps protect your organization from regulatory fines and ensures adherence to industry best practices.
Security Architecture and Tooling
The design of your security architecture refers to defensive structures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, proxies, and endpoint agents. This architectural framework is critical in defending against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Security Processes and Procedures
Security is not just about technology but also about process. Defining security procedures, such as how to respond to a potential phishing attack, creates consistency and predictability in your organization’s response to threats.
Employee & User Training and Awareness
Humans are often the weakest link in cybersecurity. Regular training and awareness programs can help employees recognize phishing attempts, malware, and other threats, reducing the likelihood of successful cyberattacks.
Conducting A Security Posture Assessment
First things first, you need to understand your current security posture. To do so, you’ll want to start with an assessment. A comprehensive assessment allows you to determine your current security standing, identify vulnerabilities, and establish a plan for enhancement.
- Inventory: Create a complete inventory of assets, including hardware, software, and data that must be protected. This establishes a clear baseline.
- Identification: Identify security gaps and vulnerabilities within your assets. This might include outdated software, unpatched systems, or insecure user practices.
- Analysis: Analyze the potential impact of identified vulnerabilities. This will help prioritize which vulnerabilities pose the most significant risk.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a risk assessment to evaluate the likelihood of threats exploiting specific vulnerabilities. Understanding both likelihood and potential damage is essential for prioritization.
- Action Items: Based on the risk assessment, create an actionable plan that outlines which vulnerabilities to address and what security measures to implement.
How To Improve Your Security Posture
Once you have assessed your current posture, the next step is improvement. Here are some strategies to strengthen your organization’s security stance:
1. Automate Asset Inventory and Management
Manual asset management is error-prone and inefficient. Automation tools provide a complete and up-to-date view of your infrastructure, making it easier to identify vulnerabilities and manage security updates.
2. Establish Policies, Procedures, and Controls
Implement robust policies and controls, such as password policies, access controls, and encryption standards. Clear, documented processes help ensure security measures are consistently applied across the organization.
3. Host Regular Employee Training and Awareness
Regular security awareness training for employees helps prevent common threats such as phishing and social engineering attacks. Keeping your team up-to-date on security best practices can reduce the likelihood of a breach.
4. Utilize Advanced Security Solutions
Employ advanced security tools like automated threat detection systems, endpoint security software, and continuous monitoring tools. These solutions help identify and mitigate emerging threats.
5. Ensure Compliance and Regulations
Ensure your organization adheres to industry-specific regulations and compliance standards. Compliance ensures legal protection and that your security practices are aligned with recognized industry standards.
How Balbix Helps Improve and Protect Your Security Posture
Balbix is at the forefront of helping organizations strengthen their security postures. The platform offers several key capabilities that support an enhanced security strategy:
- Comprehensive Attack Surface Visibility: Balbix offers complete visibility across all environments, helping you detect vulnerabilities that traditional tools might miss.
- Asset Data Correlation: By continuously ingesting, deduplicating, and correlating data across all tools, including home-grown sources, Balbix creates a unified view of your entire attack surface.
- Automated Vulnerability Identification: Balbix automates the identification of vulnerabilities and superseding patches, saving time and reducing the risk of oversight.
- Cyber Risk Quantification: Balbix quantifies cyber risk in monetary terms, helping you communicate the business impact of cyber threats to executives and boards. This makes it easier to prioritize the next best steps for risk reduction.
- Executive Reporting: With Balbix, you can track and report your progress, risk distribution, and mitigation efforts in real time, giving your leadership team complete visibility into your cybersecurity performance.
Understanding and improving your security posture protects your organization from potential cyber threats. Your organization can build a resilient cybersecurity strategy by focusing on visibility, risk management, incident response, and continual improvement. Tools like Balbix help simplify this process, ensuring you are well-equipped to face evolving threats while confidently communicating cyber risk to stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How often should a security posture assessment be conducted?
-
The frequency of security posture assessments can vary significantly from days to weeks to months depending on various factors, such as the organization’s size, the industry it operates in, and the sensitivity of the data it handles. Additionally, it’s wise to perform assessments after significant changes to the IT environment, such as new software deployments, network changes, or following a security breach.
- What is the difference between security posture and security policy?
-
Security posture refers to the overall cybersecurity strength and readiness of an organization, which includes its capabilities to identify, protect against, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber threats. It is a broad assessment of the effectiveness of the cybersecurity measures in place.
On the other hand, a security policy is a set of documented guidelines and rules that dictate how an organization and its employees should manage and protect their digital and physical resources. Security policies are components that contribute to an organization’s overall security posture.
- What role do employees play in an organization's security posture?
-
Employees play a critical role in an organization’s security posture. Human error is often cited as a leading cause of security breaches, with incidents frequently arising from clicking on phishing links, using weak passwords, or mishandling sensitive information.
Regular employee training and awareness programs are vital to a strong security posture. Such programs can educate employees about cybersecurity best practices, the importance of adhering to security policies, and how to recognize and respond to potential security threats.