Cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern business operations, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. But what exactly is cloud computing?
At its core, cloud computing allows users to access computing resources—like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the Internet. Instead of maintaining physical hardware and software on-site, businesses can rent these services from cloud providers, paying only for what they use.
Cloud computing enables organizations to operate more efficiently, scale their operations globally, and reduce IT costs. It’s also integral to innovation, with applications in developing cloud-native applications, managing data storage, testing and building apps, and much more.
Making GenAI Work for Cybersecurity
Join Nvidia and Balbix as they explore how to apply GenAI to cybersecurity, avoid common pitfalls, ensure data privacy, and uncover the true costs of building and maintaining a GenAI solution.


Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers a range of advantages that make it the go-to solution for businesses of all sizes. Below are some of the most significant benefits:
- Cost Savings: One of the main appeals of cloud computing is the cost savings it offers. Companies can reduce hardware, software, and IT management expenses by shifting to a cloud-based infrastructure. Businesses no longer need to invest heavily in on-premise data centers or maintain costly physical servers, significantly reducing capital expenses and operating costs.
- Global Scale: Cloud services allow organizations to scale operations globally. Whether expanding into new markets or growing existing operations, cloud infrastructure can be scaled up or down quickly based on demand. This elasticity is essential for meeting business goals while efficiently managing resources.
- Speed and Agility: Speed is critical in business operations. Cloud computing provides near-instant access to vast computing resources, allowing businesses to deploy solutions quickly. This agility accelerates innovation, enabling faster development and implementation of new services or products.
- Enhanced Productivity: Cloud solutions streamline IT management by automating updates, maintenance, and security patches. As a result, IT teams can focus on more strategic initiatives rather than routine tasks, leading to a more productive workforce and smoother operations.
- Improved Performance: Cloud providers use the latest technology to offer high-performance infrastructure. They operate from global data centers, ensuring low-latency access and quick load times for users worldwide.
- Reliability: Cloud computing services offer built-in redundancies, ensuring minimal downtime and data loss. Providers also offer disaster recovery options, ensuring your data and applications are available despite failure.
- Security: Security is a top priority for cloud providers. Many cloud services come with robust security features like data encryption, identity management, and threat detection, which help protect sensitive business information. However, it’s still crucial to complement cloud security with your organization’s internal cybersecurity measures.
Types of Cloud Computing
There are several cloud computing models, each catering to different business needs. Understanding these models will help you choose the right fit for your organization.
Public Cloud
Third-party providers manage the public cloud, delivering services over the Internet. It’s the most common model and is perfect for businesses looking for scalability and affordability. Public cloud providers typically handle all the infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization and can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. It offers more control over the infrastructure and is ideal for businesses that require high levels of security, such as those in regulated industries.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud environments. This model allows businesses to keep sensitive data in the private cloud while leveraging the public cloud for less critical operations. Hybrid cloud solutions offer a flexible, customizable approach to cloud computing.
Multicloud
Multicloud refers to the use of multiple cloud services from different providers. This approach allows businesses to avoid vendor lock-in and provides access to the best features from various cloud platforms.
Types of Cloud Services
Cloud computing services are generally categorized into four types, each serving different organizational functions.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides the foundational infrastructure to run applications, including servers, storage, and networking. With IaaS, businesses can avoid the hassle of managing physical infrastructure while retaining control over operating systems and applications.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS allows developers to build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. It offers a complete development environment in the cloud, streamlining the software development process.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing allows businesses to run code without provisioning or managing servers. The cloud provider automatically allocates resources as needed, allowing developers to focus solely on writing and deploying code.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the Internet, making it easy for users to access and use them from any device with an Internet connection. SaaS is ideal for businesses looking for easy-to-manage, subscription-based software solutions.
Common Uses of Cloud Computing
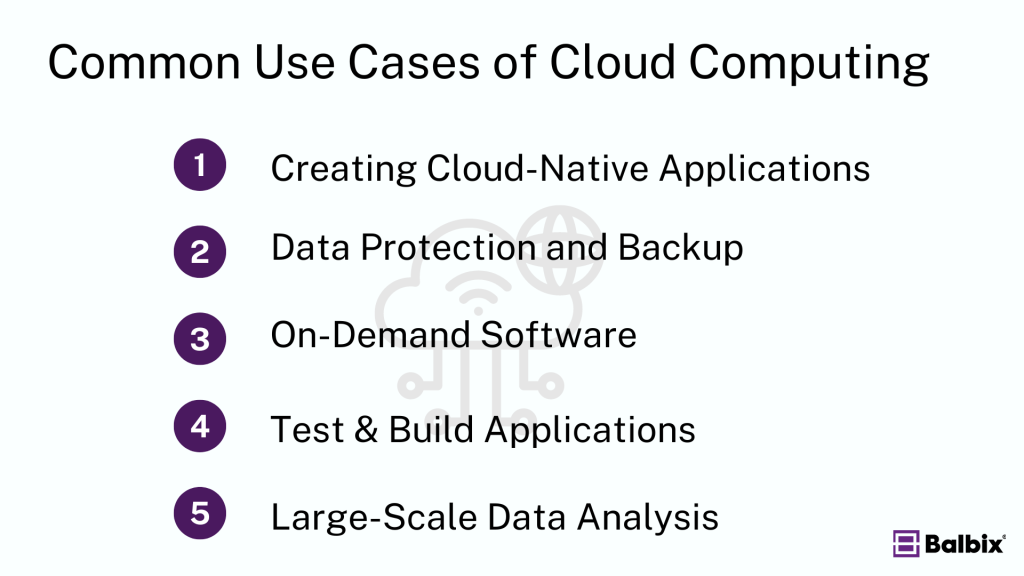
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses operate, enabling a wide variety of use cases, including:
- Creating Cloud-Native Applications: Develop, test, and deploy apps faster using cloud-based resources.
- Data Protection and Backup: Cloud solutions offer secure and reliable backup options for important data, ensuring protection from hardware failures or data breaches.
- On-Demand Software: SaaS applications provide flexibility and easy access to software, with users paying only for what they need.
- Testing and Building Applications: Cloud environments are ideal for testing and building applications in a scalable and cost-effective manner.
- Large-Scale Data Analysis: Cloud computing allows businesses to analyze massive datasets in real time, uncovering valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Cloud Computing’s Role in Cybersecurity
Cloud computing introduces both benefits and challenges for cybersecurity professionals. Cloud providers often offer advanced security tools like encryption, identity and access management (IAM), and artificial intelligence-driven threat detection, which can significantly enhance a company’s security posture.
However, it’s important to remember that security is a shared responsibility. While cloud providers handle the security of the infrastructure, businesses are responsible for securing data, managing user access, and maintaining compliance with industry regulations.
Balbix offers solutions to help businesses manage their cybersecurity in the cloud. Our AI-powered platform provides complete visibility into an organization’s security posture, allowing security teams to identify and prioritize risks across cloud environments. Balbix integrates business context with an advanced AI model to enable enterprises to better manage their exposures and mitigate potential threats.
Cloud computing continues transforming businesses’ operations, providing unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and security. Cloud solutions are essential for modern enterprises, from cost savings to improved performance and cybersecurity. As cloud adoption grows, leveraging tools like Balbix can ensure that your cloud infrastructure remains secure, efficient, and aligned with business objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How does cloud computing impact remote work?
-
Cloud computing significantly enhances remote work capabilities by providing employees access to data and applications from anywhere, anytime, and on any device with an internet connection. This flexibility improves collaboration among team members in different locations and supports a more agile, responsive work environment.
- How does cloud computing enhance cybersecurity?
-
Cloud computing enhances cybersecurity by offering advanced security measures that many organizations might be unable to implement independently. Providers invest heavily in security technologies such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits. This centralized approach to security ensures that data is better protected against breaches and cyber threats.
- What are the responsibilities of businesses in cloud computing security?
-
While cloud providers ensure the security of the cloud infrastructure, businesses are responsible for securing their data within the cloud. This includes implementing strong access controls, encrypting sensitive data before uploading it to the cloud, regularly updating and patching software, and training employees on cybersecurity best practices to mitigate the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.