Cybersecurity threats are evolving faster than ever, and keeping your organization protected has never been more important. A strong vulnerability management (VM) strategy is no longer a “nice-to-have” but a must-have to safeguard your systems, data, and reputation.
This comprehensive guide to vulnerability management will cover everything you need to know—from understanding key concepts to building a robust VM program. Whether you’re an IT professional or a cybersecurity analyst, this post will help you enhance your approach to risk reduction.
What is Vulnerability Management?
Vulnerability management is a continuous process that involves identifying, assessing, prioritizing, remediating, and reporting vulnerabilities in your systems on an ongoing basis. The goal is to reduce risk and strengthen your organization’s security posture.
Why is Vulnerability Management Important?
Vulnerability management isn’t just a security measure—it’s a critical component of effective risk management that protects businesses from cyber threats and operational disruptions. Here’s why it matters:
- Avoid Attacks and Successful Exploits: Unmanaged vulnerabilities open doors for cybercriminals, allowing them to exploit weaknesses in your systems. By proactively identifying and addressing these vulnerabilities, you reduce your exposure to cyberattacks such as data breaches, ransomware, and unauthorized access. A strong VM program helps you stay ahead of attackers.
- Save Resources: Cyberattacks can be incredibly costly, not just in terms of financial losses but also in downtime, reputational damage, and the time needed to recover. Identifying and remediating vulnerabilities early prevents these threats from escalating, saving your organization valuable time, money, and energy.
- Compliance: Many industries are governed by strict regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, that require organizations to implement proactive security measures and respond to critical threats quickly. Vulnerability management is one of several methods to help you meet these compliance requirements, avoid penalties, and demonstrate your commitment to protecting sensitive data.
Adding vulnerability management to your organization’s risk management plan helps keep systems secure, compliant, and resilient. It’s not just about fixing weak spots—it’s about reducing risks, protecting what matters most, and building trust in a world where threats are always changing.
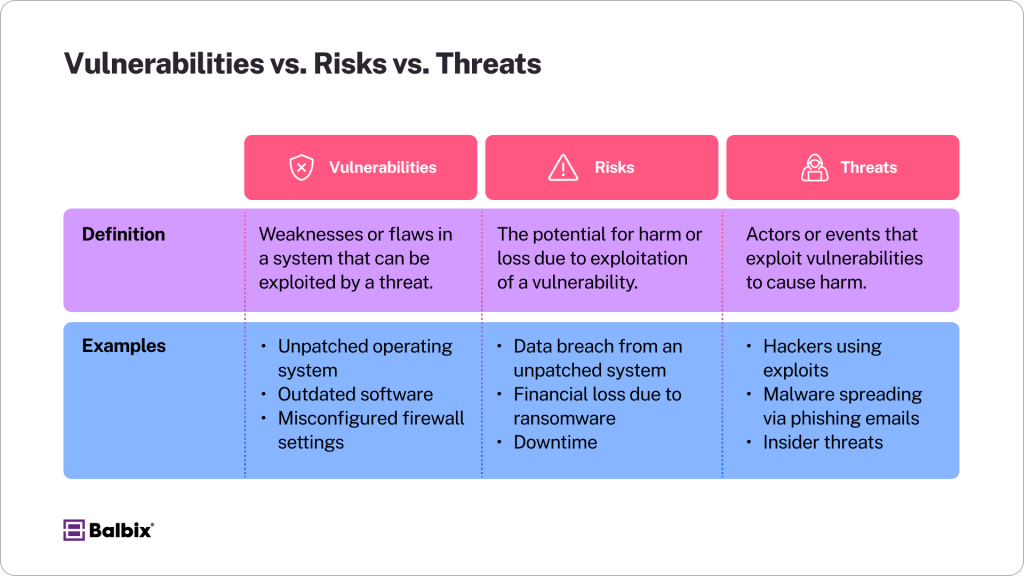
What are Vulnerabilities, Risks, and Threats?
To fully understand vulnerability management, it’s essential to grasp the distinctions between vulnerabilities, risks, and threats. Each concept plays a critical role in effectively identifying and addressing security weaknesses.
- A vulnerability is a weakness or flaw in a system, hardware, or software that an attacker can exploit. This could include an outdated operating system, an unpatched application, or even unsecured devices within a network. For example, failing to update software regularly exposes it to known exploits that hackers can easily exploit.
- Risk refers to the likelihood that a vulnerability will be exploited, which could result in damage, loss, or harm to an organization. The level of risk depends on factors such as the severity of the vulnerability, the value of the data or systems at stake, and the motivation or capability of potential attackers. For instance, an unpatched system containing sensitive customer data poses a high-risk situation because attackers are highly incentivized to gain access to that information.
- A threat is an actor, event, or circumstance that could exploit a vulnerability and cause harm. Threats can take many forms, including cybercriminals, malicious software like malware or ransomware, or even accidental actions by employees. Hackers, for example, continually search for vulnerabilities they can exploit, while phishing attacks often rely on tricking users into providing access to sensitive systems.

Common Vulnerabilities, Risks & Threats
To strengthen security, organizations need to recognize the most common vulnerabilities, risks, and threats they face:
- Outdated Software: Failing to update software or operating systems exposes systems to well-known security vulnerabilities. Attackers often scan for weaknesses in outdated software, making it a prime target for exploitation.
- Misconfigurations: Simple mistakes, such as misconfigured firewalls, improperly set access controls, or poorly designed cloud settings, can create significant security gaps. These errors can unintentionally expose sensitive assets or give attackers an easy entry point into your system.
- Phishing Attempts: Phishing remains one of the most common and effective attacks. Cybercriminals use deceptive emails, websites, or links to trick users into sharing sensitive information, such as passwords or financial details. The reliance on human error makes this a critical threat across all industries.
- Lack of Employee Awareness: Even with strong technical security measures, employees can inadvertently create vulnerabilities if they are not trained to recognize or respond to threats like phishing, weak passwords, or suspicious activity.
Understanding the differences between vulnerabilities, risks, and threats—and how they manifest in real-world scenarios—equips organizations to identify and address their weak spots more effectively.
The Difference Between Known and Unknown Vulnerabilities
Not all vulnerabilities are created equal, and understanding the distinction is crucial for protecting your systems:
- Known Vulnerabilities are publicly disclosed and listed in databases like the CVE List (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures). These vulnerabilities are well-documented, and in many cases, patches or updates from software vendors are readily available.
- Unknown Vulnerabilities are weaknesses in systems or software that have not yet been discovered by security researchers, vendors, or attackers. These vulnerabilities pose significant risks because they remain unaddressed, exposing systems to exploitation. While not all unknown vulnerabilities are actively targeted, their presence highlights the importance of proactive security measures like vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and continuous monitoring to identify and mitigate risks before they can be exploited.
Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) vs Traditional Vulnerability Management
Traditional vulnerability management often follows a flat approach—treating all identified vulnerabilities with the same level of urgency. While this ensures attention across systems, it can waste resources on low-risk issues.
What is Risk-Based Vulnerability Management?
Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) is a strategic approach to identifying and addressing system vulnerabilities by focusing on those that pose the greatest risk. Instead of treating all vulnerabilities equally, RBVM prioritizes them based on factors such as their potential impact, the likelihood of exploitation, and the importance of the affected systems.
This targeted approach ensures that critical flaws are addressed first, helping organizations optimize resources while maximizing security. By aligning vulnerability management efforts with real-world risks, RBVM enables teams to stay ahead of potential threats and protect their most valuable assets.
Implementing RBVM
- Use threat intelligence to analyze active exploits in the wild, identifying which threats are most prevalent and pose the greatest risk to your organization. Stay updated on evolving attack trends to mitigate potential breaches effectively.
- Assess vulnerabilities in relation to critical assets like customer data, intellectual property, or essential systems. Determine which vulnerabilities could have the most significant impact if exploited, ensuring that your resources are focused where they matter most.
- Automate prioritization to speed up response time, leveraging tools and software that rank vulnerabilities based on severity and relevance. This ensures your team can address high-risk threats quickly and efficiently.
Vulnerability Management vs. Vulnerability Assessment
A common misconception is equating vulnerability management with vulnerability assessment. While closely related, these distinct processes serve different purposes in strengthening an organization’s security posture.
- Vulnerability Assessment is like taking a snapshot—it provides a one-time or periodic evaluation of your system to identify and evaluate existing weaknesses. The goal is to give a clear picture of the vulnerabilities present at a specific time, helping organizations prioritize immediate issues that need attention. However, it stops short of addressing how these vulnerabilities will be managed or resolved over time.
- Vulnerability Management, on the other hand, is an ongoing, dynamic process. It incorporates assessments as part of a larger cycle but goes much further. Vulnerability management involves continuous improvement, tracking remediation efforts, and long-term oversight to ensure the system remains secure as new threats emerge. It requires a proactive approach, integrating monitoring, patching, and regularly re-evaluating systems to mitigate current and future risks.
Consider vulnerability assessments the first crucial step in a complete vulnerability management cycle. By combining these processes, organizations can address immediate risks and implement strategies for long-term security improvements, creating a more resilient defense against evolving threats.
Building a Vulnerability Management Program
An effective Vulnerability Management (VM) program requires careful planning, the right tools, and strong cross-team collaboration to protect your organization from security risks. A well-structured program ensures that vulnerabilities are identified, prioritized, and addressed promptly, reducing the risk of potential breaches.
Key Components of a VM Program
Policies and Procedures
Start by creating clear, documented guidelines that outline how vulnerabilities will be managed. Define the steps for identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and remediating security gaps. Establish timelines for remediation based on the severity of the vulnerability and ensure everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities within the process. Clear policies are essential for consistency and accountability.
Vulnerability Management Tools
Equip your team with advanced tools and automation platforms to streamline critical tasks like vulnerability scanning, patching, and reporting. Tools like Nessus and Qualys provide comprehensive coverage, helping you monitor systems, detect issues, and prioritize fixes efficiently. Automation saves time and reduces the likelihood of human error, ensuring a more reliable VM program.
Leadership Support
Gaining buy-in from leadership is critical to the success of a VM program. Without company-wide prioritization, allocating resources and fostering collaboration across departments can be challenging.
Ensure leadership understands the importance of marrying enterprise risk management with vulnerability management and work closely with IT, operations, compliance, and other relevant teams to build a united approach. Strong support from the top helps create a culture of security awareness and makes VM a priority at every level of the organization.
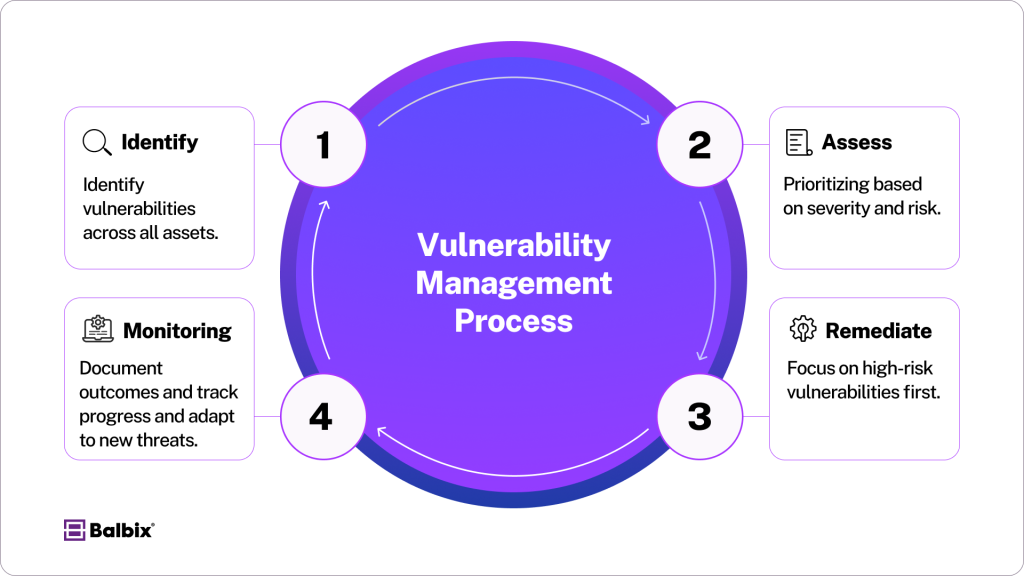
The Four Phases of Vulnerability Management
A successful Vulnerability Management (VM) program is an essential component of any organization’s security strategy, aiming to reduce risks continuously and proactively address potential threats. To achieve this, a VM program typically follows these four critical phases:
1. Scanning – Identify Vulnerabilities
This phase involves systematically identifying potential weak points in your systems.
- Set up automated vulnerability scans to run regularly and ensure no critical issues are overlooked.
- Conduct various scans, including network scans to identify open ports or misconfigurations, application scans to find software bugs, and IoT scans to secure connected devices.
- Leverage reliable tools like OpenVAS, Tenable, or Qualys to perform comprehensive scanning across your infrastructure.
- Ensure scans cover internal and external environments for a thorough evaluation.
2. Assessment – Evaluate Vulnerabilities
Once vulnerabilities are identified, the next step is to assess their significance to determine which ones demand immediate attention.
- Use scoring systems such as CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) to categorize vulnerabilities based on severity, likelihood of exploitation, and potential impact.
- Incorporate advanced threat intelligence from credible sources to gain insight into active exploits and prioritize vulnerabilities that pose the greatest risk.
- Evaluate vulnerabilities in the context of your specific environment, considering factors like asset criticality, compliance mandates, and exposure to external threats.
3. Prioritize and Remediate
Addressing vulnerabilities effectively requires prioritization based on risk and a structured remediation strategy.
- Focus remediation efforts on high-impact vulnerabilities that could cause the most damage, including those actively exploited in the wild.
- Automate remediation workflows using tools like patch management software to accelerate the patching process and reduce manual errors.
- Test patches rigorously in a controlled environment before deployment to minimize the risk of disruptions or compatibility issues.
- Document remediation steps to maintain transparency and provide a clear audit trail for compliance purposes.
4. Continuous Monitoring – Report Progress
Vulnerability management is not a one-time effort—it requires ongoing evaluation and refinement.
- Regularly track remediation outcomes to ensure vulnerabilities are addressed effectively and within established timelines.
- Use dashboards or reporting tools to provide real-time insights into your risk posture for stakeholders and leadership teams.
- Continuously monitor your environment for new vulnerabilities or system configuration changes that could introduce new risks.
- Adjust workflows and strategies based on performance metrics, system churn, and evolving threat landscapes to maintain a proactive approach to security.
Following these four phases, organizations can establish a robust VM program that reduces risk and ensures long-term security and operational resilience.
Best Practices for Successful Vulnerability Management
To strengthen your vulnerability management (VM) efforts:
- Automate Processes: Use vulnerability management tools to streamline repetitive tasks, reduce human error, and save time. Automation ensures that scanning, reporting, and remediation are consistent and accurate across your systems. Consider integration options into ticketing systems to facilitate faster assignment of remediation tasks that align with operational team processes.
- Patch Regularly: Always prioritize and apply critical updates to address vulnerabilities as soon as possible. Delaying patches can leave your systems exposed to exploits and increase security risks. Document when patches must be delayed due to business considerations and ensure a closed-loop process is defined to address deferred patches and accepted risk.
- Train Employees: Educate your team on recognizing potential threats, such as phishing emails and social engineering tactics. Since human error is one of the most common attack vectors, regular training can significantly reduce risk.
- Collaborate Externally: Work with vendors, partners, and other organizations to share threat intelligence and best practices, such as industry-specific organizations like the various Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs). Collaboration strengthens your defenses by learning about emerging risks and leveraging shared expertise.
From Vulnerability Management to Exposure Management
While vulnerability management focuses on identifying and mitigating internal weaknesses, Exposure Management (EM) takes a more comprehensive approach by addressing internal and external attack surfaces and their interconnected risks. EM expands the security scope by considering how attackers might exploit weaknesses across an organization’s digital footprint, including less visible areas like shadow IT and third-party vendor systems.
Shifting to Exposure Management
- Audit all assets, including shadow IT systems: Create a complete inventory of your digital assets, including unapproved or unnoticed systems and applications. Shadow IT can present major blind spots if left unmanaged.
- Incorporate external threat monitoring tools: These tools help you actively monitor potential external threats, such as phishing campaigns, exposed data, or unpatched vulnerabilities in your publicly accessible systems.
- Use frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK to assess the full attack surface: By leveraging standardized frameworks, you can better understand attacker behaviors and map potential attack vectors across your organization’s infrastructure.
Expanding into EM provides a more holistic view of your security posture, enabling you to proactively address risks before they can be exploited rather than reacting to vulnerabilities once they are identified.
How Balbix Simplifies Vulnerability and Exposure Management
Organizations today face an overwhelming volume of vulnerabilities and risks, with limited resources to address them. Balbix transforms this challenge into an opportunity for smarter, more efficient security operations. Here’s how Balbix helps organizations elevate their vulnerability and exposure management efforts:
1. Comprehensive Asset Inventory and Visibility
Balbix creates a dynamic and detailed inventory of your organization’s IT, OT, and IoT assets. This comprehensive visibility ensures that every device, application, and system is accounted for, leaving no room for blind spots or unknown vulnerabilities. Balbix provides a real-time understanding of your attack surface by continuously updating the inventory.
2. Context-Rich Risk Assessments
Not all vulnerabilities are created equal. Balbix leverages AI-powered analysis to assess each vulnerability in your organization’s unique risk landscape. It considers factors such as exploitability, business criticality, and threat likelihood to prioritize vulnerabilities that pose the greatest risk to your organization.
3. Automated Prioritization and Remediation Guidance
One of the biggest challenges in vulnerability management is knowing where to start. Balbix provides automated prioritization based on risk scores, helping security teams focus on the most critical issues. Additionally, the platform offers actionable remediation guidance, streamlining the patching and fixing of vulnerabilities.
4. Proactive Exposure Management
Balbix goes beyond traditional vulnerability management by incorporating exposure management capabilities. It monitors external risks, such as shadow IT, third-party vulnerabilities, and supply chain threats, ensuring your organization’s defenses are comprehensive and adaptive to new attack vectors.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Reporting
Security is not a one-time activity. With Balbix, organizations benefit from continuously monitoring vulnerabilities and exposures and intuitive dashboards that track progress and trends over time. These insights enable security leaders to measure risk reduction, demonstrate compliance, and make informed decisions to strengthen their cyber posture.
6. Streamlined Collaboration Across Teams
Effective vulnerability and exposure management requires cross-functional collaboration. Balbix facilitates this by providing clear, easy-to-understand reports and dashboards tailored to different audiences, from technical teams to C-level executives. This ensures everyone has the information to act and stay aligned on priorities
With Balbix, vulnerability and exposure management is no longer a reactive task but a proactive strategy for achieving resilience and security.
Take Control of Your Security Strategy
Vulnerability management is a continuous effort that’s crucial to reducing risk. Every step strengthens your defenses, from setting up automated scans to transitioning to exposure management.
Start small and grow your VM program over time. Looking to level up your security efforts? Consider exploring AI tools like Balbix or other platforms that simplify the process with automation.
Success in vulnerability management means staying a step ahead—and with the strategies here, your team is set to do just that.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is vulnerability management, and why is it important?
-
Vulnerability management is the ongoing process of identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and addressing security weaknesses in an organization’s systems. It’s critical because it helps reduce risk, prevent cyberattacks, ensure compliance, and protect valuable assets.
- How does vulnerability management differ from vulnerability assessment?
-
While vulnerability assessment is a one-time evaluation to identify weaknesses, vulnerability management is a continuous process. It involves tracking, prioritizing, and remediating vulnerabilities over time to maintain long-term security.
- What are the four phases of vulnerability management?
-
The four phases are:
- Scanning – Identifying vulnerabilities across systems and networks.
- Assessment – Evaluating the severity and risk of identified vulnerabilities.
- Prioritization and Remediation – Addressing high-risk vulnerabilities first.
- Continuous Monitoring – Tracking progress and adapting to new threats.
- What tools are commonly used for vulnerability management?
-
Popular tools for vulnerability management include Nessus, Qualys, OpenVAS, and Balbix. These tools help automate scanning, prioritize vulnerabilities, and streamline remediation efforts.
- What is risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM), and how does it improve traditional approaches?
-
RBVM focuses on prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their risk to your organization, considering factors like exploitability and asset criticality. Unlike traditional approaches that treat all vulnerabilities equally, RBVM ensures resources are directed toward the most significant threats.