A risk heat map (or risk heatmap) is a visual tool used in risk management to present cyber risk data in an easily digestible format. The map represents individual values in a matrix using color-coded sections to indicate varying levels of risk. Risk heat maps are helpful for organizations looking to simplify complex cyber risk assessments and prioritize areas requiring immediate attention.
Risk heat maps are intuitive and visually engaging, unlike charts or tables requiring detailed analysis. They can transform large volumes of data into actionable takeaways, making them a preferred data visualization tool for identifying, ranking, and reducing cyber risks.
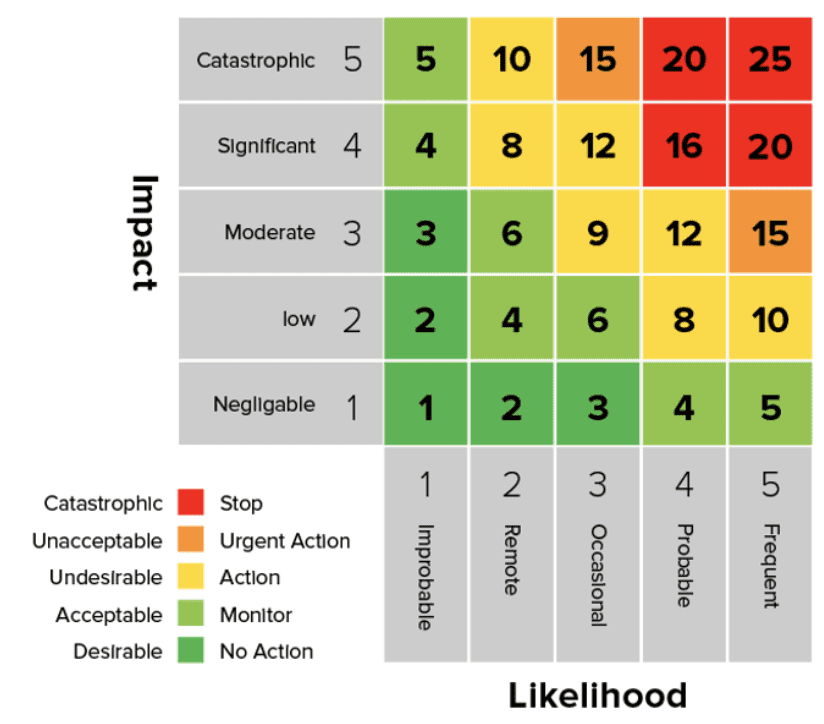
How Does a Risk Heat Map Work?
A risk heat map breaks down data into manageable visual components that help users quickly identify areas of concern.
- Axes: The heat map typically consists of two axes. The horizontal axis represents the likelihood of a cyber event occurring, while the vertical axis represents the impact that event may have on the business.
- Color Coding: The map uses a color spectrum, from green (low risk) to red (high risk), to visually represent risk levels. This color coding helps identify which risks need immediate attention and which can be monitored over time.
- Plotting of Risks: Individual risks are plotted based on their likelihood and potential impact. For example, a risk with a high likelihood but low impact might be represented by a yellow section. In contrast, a high likelihood and high impact risk would fall in the red zone, signaling immediate action.
This system allows teams to prioritize risks effectively, focusing resources where needed most.
Top Ways to Use a Risk Heat Map
Risk heat maps serve multiple purposes in cybersecurity, offering flexibility in visualizing and addressing risks. Below are some common ways risk heat maps are used:
1. Showing Risk Impact vs. Likelihood
The most straightforward application is mapping risk impact against the likelihood of occurrence. This approach helps security teams focus on the most probable and damaging risks, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
2. Comparing Breach Likelihood Across Business Areas
Risk heat maps can compare the likelihood of breaches across various departments or business units. By visualizing how different areas compare, decision-makers can identify which sectors are more vulnerable and require additional security measures.
3. Mapping IT Asset Inventory and Associated Risks
Risk heat maps can also help map the risk associated with specific IT assets, such as servers, applications, or user accounts. This visual tool can pinpoint the most vulnerable areas of your asset inventory, helping you make informed decisions about patching or updating systems.
Making GenAI Work for Cybersecurity
Join Nvidia and Balbix as they explore how to apply GenAI to cybersecurity, avoid common pitfalls, ensure data privacy, and uncover the true costs of building and maintaining a GenAI solution.


4. Monitoring Compliance Gaps and Vulnerabilities
Risk heat maps help monitor compliance with regulations and identify gaps that may expose the organization to unnecessary risk. Color-coded visuals allow quick assessments of your organization’s standing in meeting industry standards.
5. Prioritizing Response During Security Incidents
When a security incident occurs, teams can use a risk heat map to prioritize their response, focusing first on the risks that pose the most significant potential harm. This ensures that mitigation efforts are both timely and efficient.
How to Calculate Risk for Your Risk Heat Map
Risk calculation is the foundation of any helpful heat map. Traditionally, organizations relied on CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) scores and simple business impact models to calculate risk. However, this method often prioritizes based on severity alone, overlooking the specific risk posed to the business.

Advanced risk calculation methods offer a more accurate representation of risk by considering factors beyond severity. Here are key factors used in more modern approaches:
- Vulnerability Severity: How severe is the potential issue?
- Threat Level: How likely is the threat to be exploited?
- Business Impact: What effect would this risk have on business operations?
- Exposure: How exposed is the system to this particular threat?
- Mitigating Controls: What controls are already in place to reduce risk?
These factors allow organizations to focus on addressing the most pressing risks, reducing the time wasted on low-priority issues.
Key Considerations for Building a Risk Heat Map
When developing a risk heat map, several elements should be considered to make it effective:
- Important Systems and Assets: Identify which assets and systems are most important to your organization and map these areas closely.
- Data Accuracy: Risk maps are only as good as the data used to create them. Ensure data sources are reliable and up-to-date.
- Risk Tolerance: Different organizations have varying levels of risk tolerance. Your heat map should reflect this.
- Impact Categories: Define what constitutes an impact regarding financial loss, reputation damage, or operational disruption.
- Response Prioritization: Decide how to prioritize risks when they are identified on the map.
Top Benefits of Risk Heat Maps in Cybersecurity
Risk heat maps offer several advantages for managing cybersecurity threats:
- Clear Visualization of Risk: They provide an at-a-glance view of your cyber risk situation, making it easier to communicate issues to stakeholders.
- Better Risk Management: By identifying high-risk areas, security teams can make more informed decisions about where to allocate resources.
- Improved Collaboration: Risk heat maps offer a shared visual tool that can be used across departments, improving coordination during incident response and mitigation efforts.
How Automation and AI Help Risk Heat Maps
Today, many organizations use automation and AI tools to update risk heat maps continuously. This allows for more efficient risk management by keeping the heat map up-to-date with the latest data and threat intelligence. AI tools can automatically adjust risk prioritization based on changes in the environment, such as new vulnerabilities or exploits, saving teams time and effort.
How to Build a Cyber-Risk Heat Map
Building an actionable cyber-risk heat map involves several steps:
- Identify Assets: Identify all IT assets, including devices, applications, and user accounts.
- Measure Attack Surface: Gain full visibility into your organization’s attack surface and monitor it across all known threat vectors.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Continuously gather data on vulnerabilities, threat intelligence, and compensating controls.
- Plot Risks: Use the collected data to plot risks based on their likelihood and impact scores.
- Update Regularly: Ensure the map is updated frequently to reflect new data and emerging threats.
With these steps in mind, organizations can create a detailed and valuable risk heat map to help guide their cybersecurity strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the risk map used for?
-
A risk map is a tool that helps individuals or organizations understand and visualize the various risks they might face in a clear and organized way. Think of it as a map that doesn’t show places but instead shows different types of risks, how likely they are to happen, and the impact they could have.
It’s like plotting out potential problems on a chart to see which ones are minor nuisances and which could be major issues. This makes it easier to focus efforts on preventing or preparing for the big risks while keeping an eye on the smaller ones. It’s particularly useful in planning, decision-making, and risk management processes, providing a straightforward way to prioritize and tackle challenges.
- What are the disadvantages of risk heat maps?
-
While popular for visualizing potential risks and their impacts, risk heat maps have several disadvantages. Firstly, they can be pretty subjective, as categorizing risks into different levels of severity and likelihood often depends on individual judgment, leading to inconsistencies.
Additionally, these maps might oversimplify complex risks, making it difficult to understand the nuances and interconnectedness of different risks. Lastly, risk heat maps can quickly become outdated without regular updates, failing to reflect the current risk landscape accurately.
Using a risk management platform like Balbix can help solve these disadvantages.
- In which step of the risk management process do you develop a heat map?
-
Developing a heat map typically occurs during the risk assessment phase in the risk management process. This phase involves identifying and analyzing potential risks to determine their likelihood and impact.
A heat map is a visual tool that illustrates the level of risk associated with different areas or activities by using colors to represent varying degrees of risk severity. It’s a practical way to prioritize risks and make informed decisions on addressing them, making it easier for managers and stakeholders to understand and evaluate risks at a glance.


