
October 8, 2024
In this Patch Tuesday edition, Microsoft addressed 117 CVEs, including 5 Zero-Days, 3 Criticals, 113 Important and 1 Moderate. Two of the 5 Zero-Days are actively exploited in the wild.

From an Impact perspective, Escalation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities accounted for 23%, followed by Remote Code Execution (RCE) at 38% and Denial of Service (DoS) at 21%.
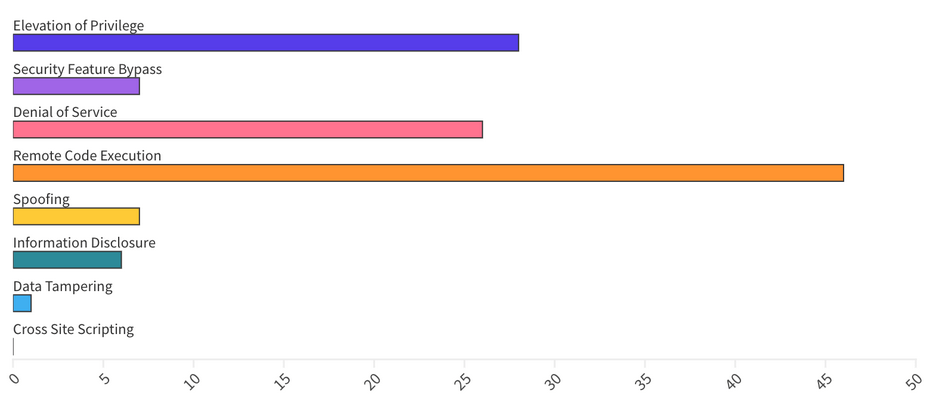
Patches for this month cover components for the following areas:
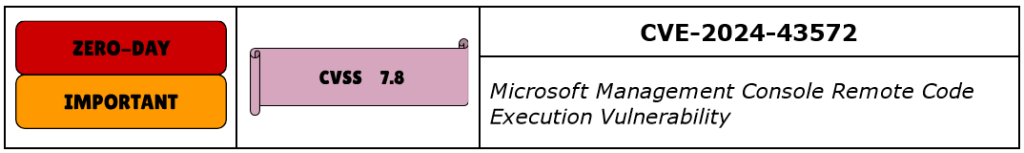
CVE-2024-43572 is a Remote Code Execution vulnerability in Microsoft Management Console, which is a tool providing users and administrators the ability to configure and manage systems. It has a CVSS score of 7.8, and it’s rated Important.
A successful exploit of this vulnerability could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on the targeted asset. The attacker could then use social engineering tactics to trick a user into uploading and opening a specially crafted file. Microsoft’s update will prevent unsigned MSC files from being used.
Microsoft has evidence that CVE-2024-43572 was exploited in the wild as a zero-day, which prompted CISA to add it to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities list – with an urgent fix date.
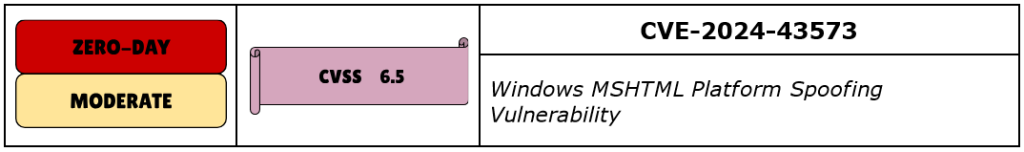
CVE-2024-43573 is a Spoofing vulnerability in Windows MSHTML Platform, a browser engine that renders web pages. It is used in Internet Explorer mode in Microsoft Edge and other applications through WebBrowser control. Even though Internet Explorer is EOL/EOS, MSHTML is still widely used, and therefore, Microsoft is still patching vulnerabilities.
Although Microsoft has not shared any details about the exploitation techniques, successful exploitation of a spoofing vulnerability cloud allows attackers to access the target system by disguising themselves as trusted sources.
Microsoft has confirmed that this vulnerability has also been successfully exploited in the wild, and CISA added it to their KEV list.
It’s important to note that the Windows MSHTML Platform has been the center of attention of the security community since this is the fourth zero-day vulnerability in this framework that was exploited in the wild in 2024. This makes it very important for organizations to consider their strategy and potentially prioritize the upgrade to newer, less problematic frameworks.
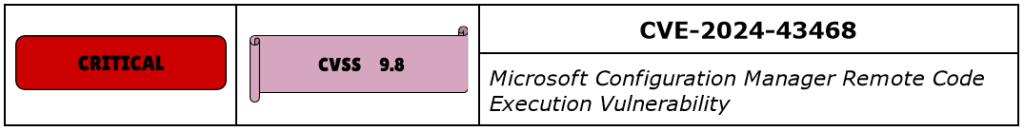
CVE-2024-43468 is a Remote Code Execution vulnerability in Microsoft Configuration Manager, part of the Microsoft Intune family, the systems management software empowering administrators to manage large groups of assets. Not to be confused with MMC. It has a CVSS score of 9.8 and is rated Critical.
A successful exploitation of this vulnerability allows an unauthenticated attacker to send specially crafted requests, resulting in executing commands on the targeted server / underlying database.
It’s important to note that to protect against this vulnerability, in addition to patching the system, you need to install an update through the product console, following their detailed Guide.
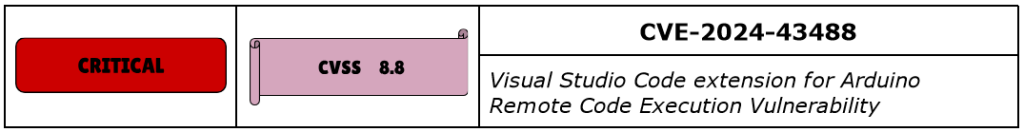
CVE-2024-43488 is a Remote Code Execution vulnerability in Visual Studio Code, which is VS Code’s Arduino extension – an open-source platform to code, build, and deploy projects for microcontrollers. It was assigned Critical severity and is related to a missing authentication control that could potentially allow attackers to execute remote code.
Microsoft is not planning to fix this vulnerability in the Visual Studio Code extension for Arduino, as the extension has been deprecated. Customers are advised to use the Arduino IDE software.
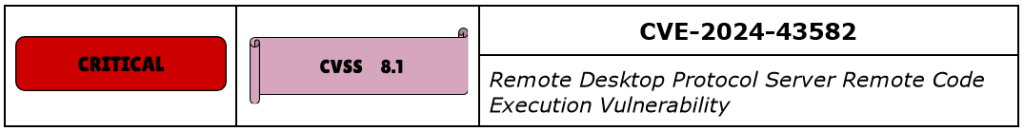
CVE-2024-43582 is a Critical Remote Code Execution vulnerability in the well-known RDP—Remote Desktop Protocol, a secure network communication protocol offered by Microsoft that allows users to execute remote operations on remote computers.
To successfully exploit this vulnerability, the attacker must craft and send malicious packets to an RPC host. This could potentially result in remote code execution on the server side with the same permissions as the RPC service.
Considering that the security best practice is to block RDP from the Internet, this should limit the exposure of most organizations to internal assets only. However, RDP is still widely used for administrative tasks. Even under these conditions, attackers could leverage this vulnerability for lateral movement within the enterprise.
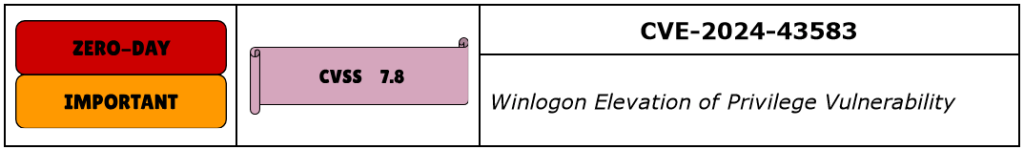
CVE-2024-43583 is an Elevation of Privilege vulnerability in Winlogon, which is Windows’ authentication utility, one of the most important security elements from a user interaction perspective. In addition to authentication, Winlogon performs a wide range of critical tasks associated with the Windows sign-in process: 1) Loads the user profile into the registry, allowing users to use the different keys for each user account. 2) Monitors user keyboard and mouse activity, triggers screen saver on inactivity and locks the PC.
This vulnerability has been publicly disclosed, but there’s no evidence that it was exploited. It has a CVSS of 7.8, is rated Important and could potentially allow an attacker to get System-level access. It’s important to note that, in addition to installing the patch, Microsoft also recommends users enable a Microsoft first-party Input Method Editor (IME) to prevent potential attackers from being able to exploit third-party IMEs during the sign-in process.
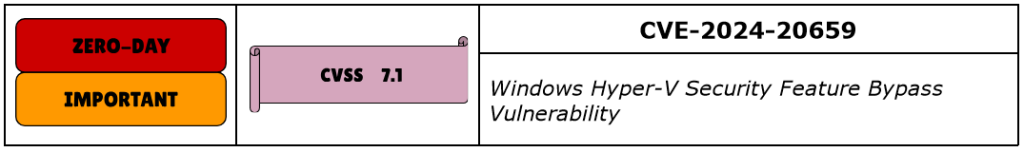
CVE-2024-20659 is a Security Feature Bypass vulnerability in Windows Hyper-V, which is Microsoft’s hardware virtualization engine, widely used especially by Enterprise organizations. It has a CVSS of 7.1, has been classified as Important and was publicly disclosed, with no evidence of being exploited.
It was marked as “less likely to be exploited,” mainly because the set of conditions that need to be met for exploitation to be successful suggests in-person user-required actions.
Successful exploitation allows the attacker to bypass the UEFI of the host asset, resulting in the compromise of both the hypervisor itself and the secure kernel, including the guests.
| CVE | Severity | Type | CVSS | Exploitation |
| CVE-2024-20659 | Important | Security Feature Bypass | 7.1 | KNOWN EXPLOIT |
| CVE-2024-30092 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-37976 | Important | Security Feature Bypass | 6.7 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-37979 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.7 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-37982 | Important | Security Feature Bypass | 6.7 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-37983 | Important | Security Feature Bypass | 6.7 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-38029 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-38097 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.1 | Unlikely |
| CVE-2024-38124 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 9 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-38129 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-38149 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-38179 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-38212 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-38229 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.1 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-38261 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-38262 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-38265 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43453 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43456 | Important | Data Tampering | 4.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43468 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | 9.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43480 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43481 | Important | Spoofing | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43483 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43484 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43485 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43488 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43497 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43500 | Important | Information Disclosure | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43501 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43502 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.1 | More Likely |
| CVE-2024-43503 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43504 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43505 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43506 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43508 | Important | Information Disclosure | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43509 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | More Likely |
| CVE-2024-43511 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43512 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43513 | Important | Security Feature Bypass | 6.4 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43514 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43515 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43516 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43517 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43518 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43519 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43520 | Important | Denial of Service | 5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43521 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43522 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43523 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 6.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43524 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 6.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43525 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 6.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43526 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 6.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43527 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43528 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43529 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.3 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43532 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43533 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43534 | Important | Information Disclosure | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43535 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43536 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 6.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43537 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43538 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43540 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43541 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43542 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43543 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 6.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43544 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43545 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43546 | Important | Information Disclosure | 5.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43547 | Important | Information Disclosure | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43549 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43550 | Important | Spoofing | 7.4 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43551 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43552 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.3 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43553 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.4 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43554 | Important | Information Disclosure | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43555 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43556 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | More Likely |
| CVE-2024-43557 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43558 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43559 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43560 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | More Likely |
| CVE-2024-43561 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43562 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43563 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43564 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43565 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43567 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43570 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.4 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43571 | Important | Spoofing | 5.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43572 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | KNOWN EXPLOIT |
| CVE-2024-43573 | Moderate | Spoofing | 6.5 | KNOWN EXPLOIT |
| CVE-2024-43574 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.3 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43575 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43576 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43581 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.1 | More Likely |
| CVE-2024-43582 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | 8.1 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43583 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | KNOWN EXPLOIT |
| CVE-2024-43584 | Important | Security Feature Bypass | 7.7 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43585 | Important | Security Feature Bypass | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43589 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43590 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43591 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 8.7 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43592 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43593 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43599 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43601 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.1 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43603 | Important | Denial of Service | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43604 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.7 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43607 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43608 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43609 | Important | Spoofing | 6.5 | More Likely |
| CVE-2024-43611 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43612 | Important | Spoofing | 7.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43614 | Important | Spoofing | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-43615 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.1 | More Likely |
| CVE-2024-43616 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2024-6197 | — | Remote Code Execution | 7.5 | KNOWN EXPLOIT |
| CVE-2024-7025 | — | Remote Code Execution | 9.8 | — |
| CVE-2024-9369 | — | Remote Code Execution | 9.8 | — |
| CVE-2024-9370 | — | Remote Code Execution | 9.8 | — |
ADOBE has released patches covering a wide range of products and vulnerabilities. The most important are CVE-2024-41869 (CVSS 7.8) and CVE-2024-45112 (CVSS 8.6)—two critical memory corruption flaws in Acrobat and PDF Reader that could lead to arbitrary code execution on compromised systems.
GITLAB has also made important updates, especially CVE-2024-6678, a CVSS 9.9 vulnerability that allows attackers to execute pipeline actions as regular users. CVE-2024-6678 is also important as it allows attackers to shut down environments remotely, without user interaction, without needing to elevate privilege. The list of fixed vulnerabilities is quite long, including CVE-2024-8640, CVE-2024-8635, CVE-2024-8124, and CVE-2024-8641, all high-severity vulnerabilities with potential impacts ranging from service disruption to unauthorized command execution and data compromise.
CISCO has released patches for 11 vulnerabilities for IOS and IOS XE products, with issues ranging from DoS to RCE. Particularly interesting is CVE-2024-20350, which could allow a remote attacker to intercept traffic between SSH clients and the Catalyst Center SSH server. CVE-2024-20381 in the Network Services Orchestrator could allow a remote authenticated attacker to send malicious requests, create a new account, or escalate privileges.
As always, you should patch everything as soon as possible… 😉
But that’s a lot easier said than done. The strategy is prioritizing what matters most and reducing the vulnerabilities with the greatest business impact. For this, organizations must improve how they measure, quantify, prioritize, and communicate risk. Balbix offers the following AI-powered capabilities:
#1 – CAASM > Understand your attack surface. An accurate & up-to-date inventory of on-premises, cloud, IoT/OT assets and software bill of materials (SBOM) is fundamental. Additionally, organizations need to understand:
#2 – RVBM > Prioritize and remediate critical vulnerabilities. Use severity, threat intelligence, asset exposure, compensating controls and business context to understand which vulnerabilities are exploited and the financial impact of it (if exploited) to your organization. Use this data to prioritize ruthlessly.
#3 – CRQ > Quantify Cyber Risk. Using a language that is easily understandable by all, i.e., monetary or currencies. It’s the only way to effectively communicate and compare risk across all different environments, software, geos, business units, etc.
But the true magic of Balbix happens when you put all these together:
The Balbix Platform started doing its homework as soon as vendors announced CVEs. No human interaction is needed. It’s all driven by AI. It learned about the new CVEs and the Cyber Threat Intelligence associated with each of them, and it correlated with each asset’s technical and business context to calculate the Balbix scores.
This way, Risk-Based Prioritization is already done, and Balbix customers can simply start a Patch Prioritization workflow and automatically get the latest KB that needs to be installed on a set of assets / OS.
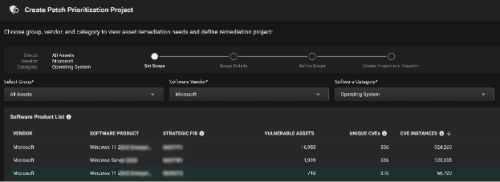
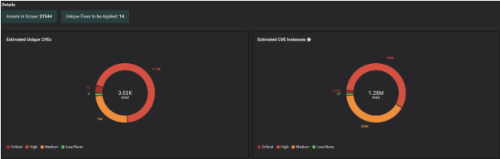
This way, Balbix customers have a clear understanding of the assets in scope, unique CVE detections, unique patches to be applied, etc., and most importantly, the priority in which patches need to be installed to burn down risk in the most efficient way possible.
If you want to learn more, please sign up for a Balbix demo.