
January 15, 2025
In this Patch Tuesday edition, Microsoft addressed 159 CVEs, including 8 Zero-Day, 10 Criticals, 147 Important — with 3 Zero-Days actively exploited in the wild and 5 others publicly disclosed.

From an Impact perspective, Escalation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities accounted for 39%, followed by Remote Code Execution (RCE) at 36% and Denial of Service (DoS) at 12%.
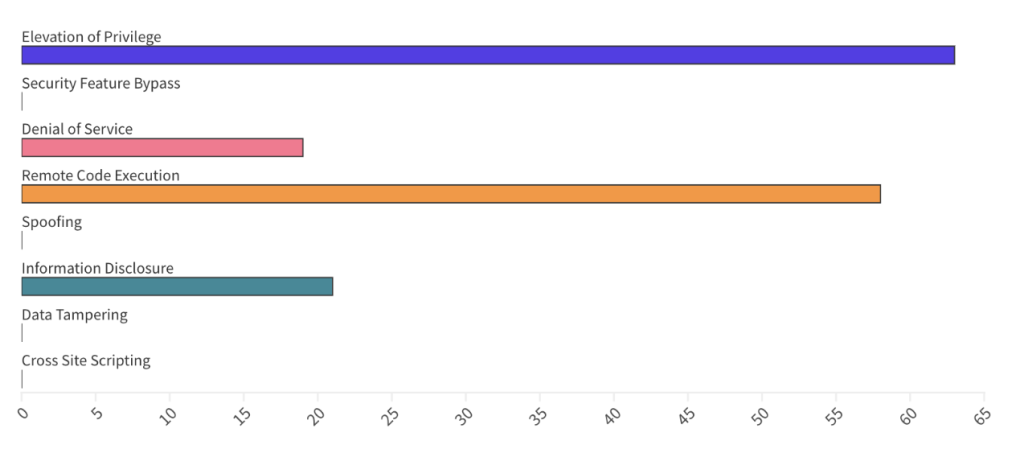
Patches for this month cover components for the following areas:
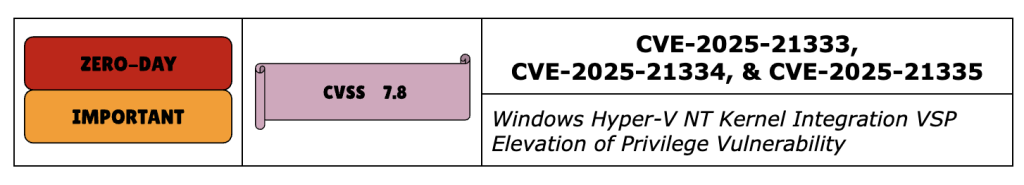
CVE-2025-21333, CVE-2025-21334 and CVE-2025-21335 are Escalation of Privilege vulnerabilities in VSP – Windows Hyper-V NT Kernel Integration Virtualization Service Provider. VSP resides in the root partition of a Hyper-V instance, and provides synthetic device support to child partitions over the Virtual Machine Bus (VMBus): it’s the foundation of how Hyper-V allows the child partition to trick itself into thinking that it’s a real compute engine.
All three vulnerabilities are assigned CVSS 7.8 and rated Important. A successful exploit of this vulnerability could allow an attacker to elevate privileges to SYSTEM. For those who are running Hyper-V, these vulnerabilities should be on top of their list to patch as soon as possible.
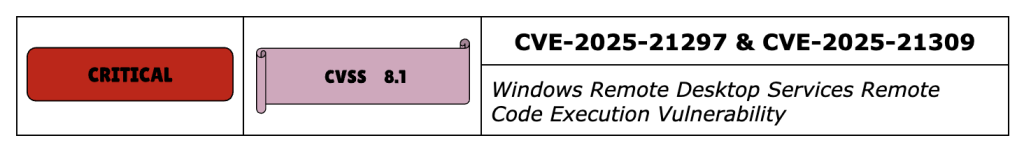
CVE-2025-21297 and CVE-2025-21309 are Remote Code Execution vulnerabilities affecting Windows Remote Desktop Services. Both have a CVSS of 8.1 and are rated Critical. Given the wide usage of RDP services, this should also be a high priority for all security professionals.
A successful exploit allows an unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code on the Remote Desktop Gateway servers remotely. The attacker must connect to the server and trigger a race condition that creates a use-after-free scenario.
Microsoft considers the exploitation of CVE-2025-21309 “More Likely,” while it considers the exploitation of CVE-2025-21297 ” less likely.”
CVE-2025-21298 is a Remote Code Execution vulnerability in Microsoft’s Windows Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) – which is a technology that allows users to insert & interact with objects created in one application within another application, essentially enabling the integration of data from different programs into a single document, like embedding an Excel spreadsheet into a Word document.
This vulnerability has a CVSS of 9.8 and is rated as Critical. A successful exploit allows a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code remotely on the target system, by building and sending a specially crafted email, which would activate when opening using a vulnerable Outlook version and parsing the RTF payload. The root cause is related to improper validation of use-entered data, leading to memory corruption.
As a workaround, Microsoft recommends configuring Microsoft Outlook to read email messages “in plain text format” instead of a rich format that will display rich content, such as photos. Although the advisory has some value for security professionals, it is highly unlikely that users and/or organizations can implement this in real life (and in real time). So, patching to the latest version should be a priority for Outlook users.
CVE-2025-21308 is a Spoofing vulnerability affecting Windows Themes. Although this vulnerability was assigned a CVSS of 6.5 and is rated as Important, it’s important to note that it could be especially used in a social engineering type attack, as many users are interested in loading custom themes on their systems.
Successful exploitation of the vulnerability requires an attacker to build, distribute and convince the user to load a specially crafted file as part of the theme. A previous patch (CVE-2024-38030) was already released for this flaw, but it did not cover all possible angles, leading to the release of this new vulnerability and patch.
The vulnerable component is, again, NTLM. Microsoft provides additional guidance on how organizations can restrict outbound NTLM traffic to remote servers: Microsoft Advisory.
CVE-2025-21275 is an Elevation of Privilege vulnerability in the Microsoft Windows App Package Installer. It has a CVSS rating of 7.8 and it’s rated Important.
An authenticated attacker needs to perform the attack. Successful exploitation allows the attacker to get SYSTEM privilege, which means that this type of vulnerability is potentially used in the late stages of an attack after the initial compromise was performed through other means.
However, given that the Windows App Package Installer is a core component of Windows systems, closely interlinked with many other elements, it’s highly recommended that this vulnerability gets additional attention and action from the security and IT teams.
| CVE | Severity | Type | CVSS | Exploitation |
| CVE-2024-50338 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.4 | — |
| CVE-2024-7344 | Important | Information Disclosure | 6.7 | — |
| CVE-2025-21171 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.1 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21172 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21173 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21176 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21178 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21186 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21187 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21189 | Important | Information Disclosure | 4.3 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21193 | Important | Information Disclosure | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21202 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.1 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21207 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21210 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 4.2 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21211 | Important | Information Disclosure | 6.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21213 | Important | Information Disclosure | 4.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21214 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 4.2 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21215 | Important | Information Disclosure | 4.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21217 | Important | Information Disclosure | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21218 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21219 | Important | Information Disclosure | 4.3 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21220 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21223 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21224 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21225 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.1 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21226 | Important | Denial of Service | 5.9 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21227 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21228 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21229 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21230 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21231 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21232 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21233 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21234 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21235 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21236 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21237 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21238 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21239 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21240 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21241 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21242 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.9 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21243 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21244 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21245 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21246 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21248 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21249 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21250 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21251 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21252 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21255 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21256 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21257 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21258 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21260 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21261 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21263 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21265 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21266 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21268 | Important | Information Disclosure | 4.3 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21269 | Important | Information Disclosure | 4.3 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21270 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21271 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21272 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21273 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21274 | Important | Denial of Service | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21275 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21276 | Important | Information Disclosure | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21277 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21278 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.2 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21280 | Important | Denial of Service | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21281 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21282 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21284 | Important | Denial of Service | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21285 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21286 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21287 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21288 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21289 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21290 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21291 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21292 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 8.8 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21293 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21294 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | 8.1 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21295 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | 8.1 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21296 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21297 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | 8.1 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21298 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | 9.8 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21299 | Important | Information Disclosure | 7.1 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21300 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21301 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21302 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21303 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21304 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21305 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21306 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21307 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | 9.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21308 | Important | Information Disclosure | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21309 | Critical | Remote Code Execution | 8.1 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21310 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21311 | Critical | Elevation of Privilege | 9.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21312 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 2.4 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21313 | Important | Denial of Service | 6.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21314 | Important | Information Disclosure | 6.5 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21315 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21316 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21317 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21318 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21319 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21320 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21321 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21323 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21324 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21326 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21327 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21328 | Important | Information Disclosure | 4.3 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21329 | Important | Information Disclosure | 4.3 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21330 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21331 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.3 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21332 | Important | Information Disclosure | 4.3 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21333 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | KNOWN EXPLOIT |
| CVE-2025-21334 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | KNOWN EXPLOIT |
| CVE-2025-21335 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | KNOWN EXPLOIT |
| CVE-2025-21336 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21338 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21339 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21340 | Important | Information Disclosure | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21341 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.6 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21343 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21344 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21345 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21346 | Important | Information Disclosure | 7.1 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21348 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.2 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21354 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21356 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21357 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 6.7 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21360 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21361 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21362 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21363 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21364 | Important | Information Disclosure | 7.8 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21365 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | More Likely |
| CVE-2025-21366 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21370 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21372 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21374 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 5.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21378 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21380 | Critical | Elevation of Privilege | 8.8 | — |
| CVE-2025-21382 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21385 | Critical | Elevation of Privilege | 8.8 | — |
| CVE-2025-21389 | Important | Denial of Service | 7.5 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21393 | Important | Information Disclosure | 6.3 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21395 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21402 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 7.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21403 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 6.4 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21405 | Important | Elevation of Privilege | 7.3 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21409 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21411 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21413 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
| CVE-2025-21417 | Important | Remote Code Execution | 8.8 | Less Likely |
As always, you should patch everything as soon as possible… 😉
But that’s a lot easier said than done. The strategy prioritizes what matters most and reduces the vulnerabilities with the greatest business impact. For this, organizations must improve how they measure, quantify, prioritize, and communicate risk. Balbix offers the following AI-powered capabilities:
#1 – CAASM > Understand your attack surface. An accurate & up-to-date inventory of on-premises, cloud, IoT/OT assets and software bill of materials (SBOM) is fundamental. Additionally, organizations need to understand:
#2 – RVBM > Prioritize and remediate critical vulnerabilities. Use severity, threat intelligence, asset exposure, compensating controls and business context to understand which vulnerabilities are exploited and the financial impact of it (if exploited) to your organization. Use this data to prioritize ruthlessly.
#3 – CRQ > Quantify Cyber Risk. Using a language that is easily understandable by all, i.e., monetary or currencies. It’s the only way to effectively communicate and compare risk across all different environments, software, geos, business units, etc.
But the true magic of Balbix happens when you put all these together:
The Balbix Platform started doing its homework as soon as vendors announced CVEs. No human interaction is needed. It’s all driven by AI. It learned about the new CVEs and the Cyber Threat Intelligence associated with each of them, and it correlated with each asset’s technical and business context to calculate the Balbix scores.
This way, Risk-Based Prioritization is already done, and Balbix customers can simply start a Patch Prioritization workflow and automatically get the latest KB that needs to be installed on a set of assets / OS.
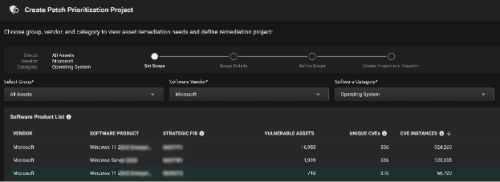
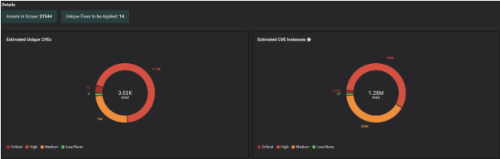
This way, Balbix customers clearly understand the assets in scope, unique CVE detections, unique patches to be applied, etc., and most importantly, the priority in which patches need to be installed to burn down risk in the most efficient way possible.
If you want to learn more, please sign up for a Balbix demo.